All Blogs
Healthcare SaaS Application Pentesting Checklist to Secure Hospital Systems

Quick Summary: Healthcare SaaS applications store sensitive patient and financial data, making them prime targets for cyberattacks. This pentesting checklist outlines the key steps to identify vulnerabilities, secure APIs and cloud systems, and maintain HIPAA compliance. Use it as a practical guide to strengthen your healthcare SaaS security and protect critical medical information.
Healthcare SaaS applications are reshaping the way hospitals and clinics deliver care. From electronic medical records (EMRs) to telehealth platforms, these solutions streamline operations and improve patient outcomes. And with the global healthcare SaaS market projected to surpass $74.74 billion by 2030, it’s clear that reliance on these systems will only continue to grow.
Yet with this growth comes a hidden cost, rising cyber risk. The healthcare SaaS platforms manage protected health information (PHI) and connect to multiple third-party APIs. One overlooked vulnerability in this system can open the door to cyber-attacks, compliance fines, and patient data exposure. It’s no surprise that IBM report ranked healthcare as the costliest sector for breaches, averaging $10.93 million per incident.
This is where penetration testing becomes one of the keyways to secure your system. Far more than a checkbox, it gives healthcare SaaS companies a way to detect weaknesses and prevent sensitive data exposure.
In this blog, we’ll break down a complete healthcare penetration testing checklist for SaaS apps. You’ll learn the vulnerable areas to test, the steps involved, and how you can ensure compliance-ready security.
Detect and fix vulnerabilities before attackers strike. Sign Up Free
On This Page
- Why Healthcare SaaS Applications Need Penetration Testing?
- What is the Scope of a Healthcare SaaS Penetration Testing?
- The Complete Healthcare SaaS App Pentesting Checklist
- Five Steps of Healthcare SaaS Penetration Testing
- How ZeroThreat Simplifies Pentesting for Healthcare SaaS Apps
- Conclusion
Why Healthcare SaaS Applications Need Penetration Testing?
Healthcare SaaS applications carry far more risk than a regular business app. They handle patient records, EMRs, billing details, and often connect directly to hospital networks. A single vulnerability can expose protected health information (PHI) and cost you compliance penalties. This makes penetration testing a non-negotiable practice to carry out.
If we dive more into it, here are the three reasons that will help you understand the need for healthcare SaaS app pentesting.
Regulatory Compliance Requirements
Unlike standard software, healthcare SaaS platforms operate in a highly regulated space. HIPAA, GDPR, and HITRUST compliance regulators demand that healthcare SaaS applications have strong system security. A healthcare penetration testing checklist helps ensure SaaS security by detecting vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
Complexity of Healthcare Systems
Another reason to perform automated pentesting is the complexity of modern healthcare systems. APIs link EMR platforms, mobile apps, and third-party services together. If one weak integration is left unchecked, it can become the entry point for a breach. Regular penetration testing of these applications ensures data security and reduces the risk of successful attack.
Building Patient and Provider Trust
Finally, there’s the matter of trust as well. Patients and healthcare providers expect SaaS apps to be secure at all costs. A hospital penetration testing checklist validates the security controls and strengthens confidence in the service. Without it, both compliance and reputation are at risk.
What is the Scope of a Healthcare SaaS Penetration Testing?
The scope of penetration testing in healthcare SaaS goes far beyond just scanning an app for bugs. It is about evaluating every layer, from hospital networks to APIs that move EMR records between systems. A well-defined scope ensures that no vulnerable endpoint is missed, and the test includes real-world risks hospitals and healthcare SaaS applications face.
Here is what you should include in your scope of pentesting for healthcare SaaS applications:
1. Core Application: Web, Mobile, and APIs
Your SaaS app, whether accessed via browser, iOS, Android, or integrated through APIs, is the entry point for hackers. You should test all user roles, including patient, clinician, admin, and billing staff. Pay special attention to:
- Authentication and session management (for example, can a logged-out user reuse a token?)
- Multi-tenancy isolation (can Hospital A see Hospital B’s data?)
- IDOR (Insecure Direct Object Reference) vulnerabilities (changing a patient ID in a URL should not grant access to another record)
- Input validation in text fields, lab result uploads, or prescription modules
If your app syncs with EMRs like Epic via HL7, those interfaces must be tested as well.
2. Cloud Infrastructure and Configuration
Most healthcare SaaS runs on AWS, Azure, or GCP. But “cloud secure by default” is a myth. Security misconfigurations here leak PHI faster than app bugs. That is why you should include the following in your scope:
- IAM policies (over-permissioned roles are common)
- S3 buckets, Blob Storage, or Cloud Storage. Check for public access or missing encryption
- VPC and network segmentation between dev, staging, and prod
- Secrets management (are API keys hardcoded or exposed in logs?)
A single open S3 bucket has caused multiple HIPAA breaches. Don’t be next.
3. Third-Party Integrations and Dependencies
Healthcare SaaS rarely works in isolation. You likely integrate with:
- Payment processors (for co-pays or billing)
- Identity providers (Okta, Azure AD)
- Analytics or support tools (for example, Zendesk, Segment)
Each integration expands your attack surface, so you need to test:
- OAuth scopes (are you requesting more access than needed?)
- Webhook validation (can an attacker spoof a lab result callback?)
- JavaScript SDKs loaded in your app
Remember: if a third party accesses PHI, they are in your BAA (Business Associate Agreement) and should be included in your pen test scope.
4. Secure Development and CI/CD Pipeline
Pen testing is not just about the running app. It is about how it is built. Ask your team:
- Do dependency scans run before merge? (Log4j-style flaws still happen)
- Is secrets scanning enabled in GitHub or GitLab?
- Are containers scanned for vulnerabilities before deployment?
If your pipeline lacks these controls, your pen test should flag the process.
5. Data Handling: At Rest, In Transit, and in Use
HIPAA requires encryption of ePHI, but implementation matters. Verify:
- TLS 1.2 or higher is enforced everywhere (no legacy SSL)
- Database fields containing PHI are encrypted, not just the disk
- Data deletion workflows purge records, not just hide them
Bonus: test backup and export functions. We have seen PHI dumped into unsecured CSVs during “data portability” requests.
6. What’s Not in Scope (And Why That Matters)
Be clear about boundaries upfront. Typical exclusions include:
- Underlying cloud provider infrastructure (AWS manages the hypervisor, you manage your instance)
- Physical security of data centers (handled by your CSP)
- Medical devices you do not control (unless you are directly integrating with them)
Document these exclusions in your pen test agreement. It protects you and keeps the tester focused on what you actually own.
Secure your SaaS from cyberattacks by detecting security flaws most precisely. Run a Pen Test
The Complete Healthcare SaaS App Pentesting Checklist
Penetration testing in healthcare SaaS is about more than checking for obvious flaws. Below are key areas every healthcare organization should prioritize in its penetration testing checklist.
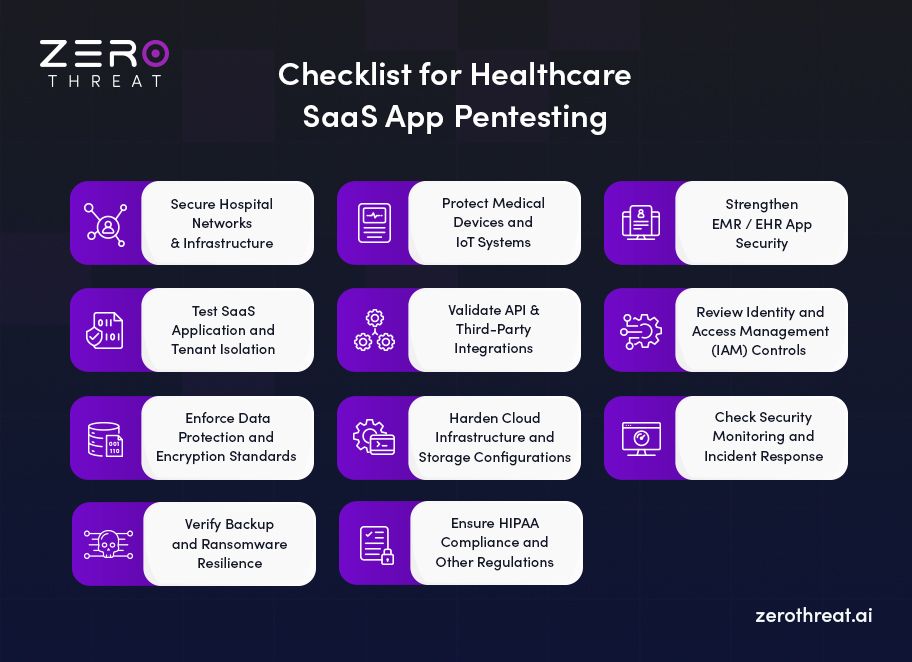
1. Secure Hospital Networks and Infrastructure
Hospital networks connect EMRs, lab systems, and SaaS platforms, creating multiple attack paths. Penetration testing should focus on firewalls, VPNs, segmentation, and real-time monitoring to spot weaknesses. Legacy systems and unpatched software must be included, as they often become entry points. A strong network foundation reduces the risk of breaches and safeguards patient data.
2. Protect Medical Devices and IoT Systems
Connected medical devices, from monitors to infusion pumps, can be exploited if left unsecured. Testing should include firmware reviews, authentication checks, and communication protocol validation. Network segmentation limits lateral movement if a device is compromised. Protecting IoT systems ensures patient safety and prevents unauthorized access to hospital data.
3. Strengthen EMR / EHR Application Security
EMR/EHR applications are a primary target because they store sensitive patient records. Security testing should cover SQL injections, broken access controls, session handling, and API vulnerabilities. Every integration with other systems needs evaluation to prevent data leaks. Robust application security keeps PHI safe and supports HIPAA compliance.
4. Test SaaS Application and Tenant Isolation
Healthcare SaaS platforms often serve multiple clients on the same infrastructure, making isolation critical. Penetration testing should verify that one tenant cannot access another’s data. Security reviews should include session management, data segregation, and configuration settings. Proper tenant isolation ensures patient data stays private and regulatory requirements are met.
5. Validate API and Third-Party Integrations
APIs connect EMRs, web apps, and third-party services, creating potential attack surfaces. Testing should check authentication, authorization, and input validation for every integration. Vulnerabilities here can allow attackers to steal PHI. Validating integrations ensures secure data flow and prevents breaches across connected systems.
6. Review Identity and Access Management (IAM) Controls
Healthcare systems involve multiple roles, which include doctors, nurses, admins, and patients, each needing controlled access. A pentest should verify MFA (Multi-Factor Authentication), role-based access, and privilege escalation protections. Strong IAM ensures security against sensitive data exposure while supporting compliance with HIPAA and SaaS security compliance standards.
7. Enforce Data Protection and Encryption Standards
Healthcare data should remain secure at rest and in transit to prevent breaches. Penetration testing must verify encryption protocols, key management, and secure storage practices. Sensitive PHI and EMR records require strong protection against unauthorized access. Using sensitive data scanner allows you to safeguard patient information with ease.
8. Harden Cloud Infrastructure and Storage Configurations
Most healthcare SaaS solutions rely on cloud services, which must be configured securely. Testing should include permission reviews, storage access controls, and vulnerability scanning of cloud components. Misconfigurations can expose critical patient data or enable ransomware attacks. Properly hardened cloud infrastructure ensures both operational security and regulatory compliance.
9. Check Security Monitoring and Incident Response
Early detection is key to preventing breaches from escalating. Penetration testing should review logging, monitoring systems, alerting, and incident response workflows. Simulated attacks help identify gaps in threat detection and response speed. Strong monitoring and response controls minimize damage and ensure quick recovery in case of security incidents.
10. Verify Backup and Ransomware Resilience
Reliable backups and recovery plans are required to minimize downtime during attacks. Penetration testing should check backup integrity, restoration procedures, and ransomware recovery readiness. Ensuring these systems function correctly prevents permanent data loss.
11. Ensure HIPAA Compliance and Other Regulations
Healthcare organizations must meet strict regulatory standards to protect patient data. Testing should map security controls against HIPAA, HITRUST, and GDPR requirements. Detecting security and compliance gaps before audits prevent hefty fines and reputational damage.
Five Steps of Healthcare SaaS Penetration Testing
Penetration testing needs a structured approach to identify vulnerabilities without disrupting operations. The following five steps outline a practical process that ensures security, compliance, and patient data protection.
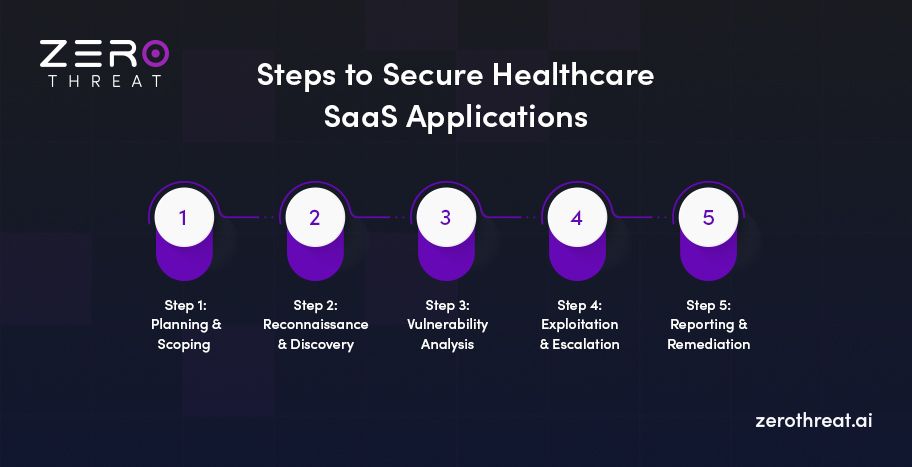
Step 1: Planning & Scoping
Before you start testing, clearly define what systems, SaaS modules, and hospital networks are in scope. Identify sensitive assets such as EMRs, APIs, and third-party integrations. Set goals aligned with HIPAA compliance, SaaS security controls, and risk tolerance.
Step 2: Reconnaissance & Discovery
This step involves gathering information about the SaaS environment, hospital network topology, and connected devices. Testers should look for exposed endpoints, public IPs, open ports, and API documentation. Understanding system architecture helps anticipate potential attack paths.
Step 3: Vulnerability Analysis
Automated and manual scans identify weaknesses in EMR applications, cloud storage, APIs, and hospital networks. Tools help detect misconfigurations, unpatched software, and insecure protocols. Findings are analyzed to prioritize risks based on potential impact and likelihood. It will help security teams focus on security gaps that could lead to PHI breaches or compliance violations.
Step 4: Exploitation & Escalation
Here, testers attempt to safely exploit identified vulnerabilities and know their impact. This includes lateral movement within hospital networks, privilege escalation in EMRs, or API misuse. The goal is to find flaws and understand how attackers can leverage them. With this step, you will be able to know whether security controls effectively protect sensitive data or not.
Step 5: Reporting & Remediation
The final step documents all findings, maps them to HIPAA, HITRUST, and GDPR, and provides actionable remediation guidance. Prioritized recommendations can help SaaS teams fix critical gaps quickly. Retesting allows you to fix and reduce the risk. Clear reporting also demonstrates compliance and strengthens patient trust in the SaaS platform.
How ZeroThreat Simplifies Pentesting for Healthcare SaaS Apps
Healthcare SaaS apps need security that’s fast, accurate, and compliance ready. Manual testing alone can’t deliver that at scale. ZeroThreat uses AI and automation to simplify penetration testing without slowing your team down.
Here’s how ZeroThreat makes penetration testing easy and efficient:
- Automated Scans: One-click scans for web apps and APIs with no complex configuration required.
- API & Web Coverage: Detects hidden APIs, endpoints, and logic flaws across healthcare integrations.
- High Accuracy: 98.9% accuracy with near-zero false positives, so teams fix real issues faster.
- AI-Driven Remediation: Provides remediation steps with code examples to accelerate secure patching.
- Compliance-Ready Reports: Reports mapped to HIPAA, GDPR, and PCI DSS for quick audit readiness.
- Fast Turnaround Time: Scans complete in 0.5–2 hours, enabling you to test every SDLC.
- CI/CD Integration: Plugs into DevSecOps tools to stop vulnerabilities before production.
Want to make your healthcare SaaS penetration testing effortless? Contact ZeroThreat
Conclusion
Healthcare SaaS platforms hold sensitive patient records and financial details. That makes it favorable for hackers to launch cyberattacks and gain personal benefit. But with a penetration testing checklist for healthcare SaaS apps, you can ensure secure systems so that attackers can’t exploit them.
A comprehensive checklist helps identify vulnerabilities across hospital networks, EMR applications, APIs, and cloud storage. It also ensures compliance with HIPAA and other healthcare regulations while strengthening patient trust. By pentesting regularly and following best practices, you can stay one step ahead of attackers and safeguard both data and reputation.
If you don’t want to waste your time with manual pentesting and ensure security, try ZeroThreat's automated penetration testing tool. It will help you simulate a real-world attack on your own SaaS app, which will let you know the potential vulnerabilities with near-zero false positives.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should healthcare SaaS companies run penetration tests?
At a minimum, healthcare SaaS companies should test once a year, but many run them quarterly or after major updates. Since these apps handle sensitive PHI, more frequent testing helps catch new risks early. Platforms like ZeroThreat make continuous testing practical by automating much of the process.
What is the cost of penetration testing for healthcare SaaS applications?
Is HIPAA compliance verified through penetration testing?
How does hospital pen testing differ from a general pen test?
What vulnerabilities are commonly found in hospital systems?
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


