Solution Security
ZeroThreat prioritizes solution security by implementing robust measures to ensure the safety and integrity of customer data. We follow industry-leading standards and best practices for security solutions. We comply with regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI DSS to ensure data privacy and protection. Our security measures align with ISO 27001 guidelines for information security management systems, demonstrating our commitment to maintaining the highest security standards.
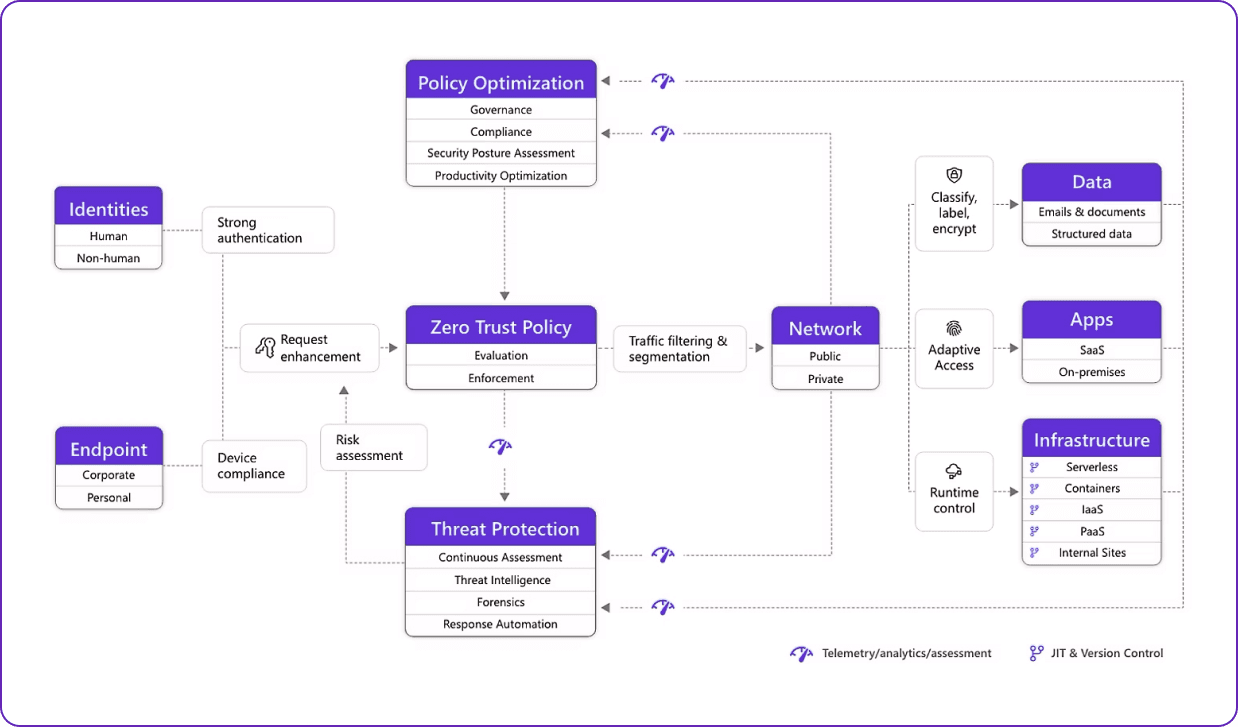
Zero Trust Architecture Model We Follow
ZeroThreat adheres to the Zero Trust Architecture principles and incorporates security best practices into its guidance, including:
- Microsoft CyberSecurity Reference Architecture
- Microsoft Cloud Security Benchmark
- The Cloud Adoption Framework
- The Well-Architected Framework
- Microsoft Security Best Practices
Principles That ZeroThreat Follows

Never Trust, Always Verify
Every access request is fully authenticated, authorized, and encrypted before granting access, even from trusted users and devices.

Least Privilege
Limit user access with Just-In-Time and Just-Enough-Access (JIT/JEA), risk-based adaptive policies, and data protection.

Continuous Monitoring
All Activity is monitored for suspicious behavior.
Implemented Security Technologies
- Identity and Access Management: IAM controls who can access what resources
- Multi-Factor Authentication: MFA requires users to provide multiple forms of identification to verify their identity.
- Network Segmentation: Network segmentation divides the network into smaller zones, making it more difficult for attackers to move laterally.
- Threat Protection: Cloud native filtering and protection for known threats.
- Data Encryption: To protect sensitive data from unauthorized users.
- Enumerating the secure transaction protocol such as TLS 1.3.
- Utilizing cryptographic algorithms like AES, 3DES, and RSA for data encryption and setting the acceptable key lengths for use with each algorithm based on the sensitivity of information transmitted/stored.
- Security Analytics: Azure Monitor, Log Analytics, Microsoft Defender for Cloud, Microsoft Sentinel and other Azure tools are used for security analytics or incident reporting.
Security Protection
- Protecting Security of Assets
- Data Classifications: Data security is to be applied based on the classification of the data.
- Confidential (Class 3): Vulnerability data is confidential data.
- Private (Class 2): Organization Users data is private data.
- Sensitive (Class 1): Application login credentials, steps and request payloads.
- Public (Class 0): Publicly accessible data.
- Data States: It’s important for us to protect the data at all data states, including while it is at rest, in motion and in use.
- Data at Rest: Data at rest is any encrypted data stored on Azure Blob Storage. The encryption key is managed through Azure Key Management Service called Azure Key Vault. The application usage key management is Microsoft Management keys.
- Data in Transit: Data transmitted over the network enumerating the secure transaction protocol TLS 1.3.
- Data in Use: The admin portal application is fully stateless. The worker application flushes the buffers when the data is not used.
- Data Classifications: Data security is to be applied based on the classification of the data.
- Handling Sensitive Information and Assets
- Proper policies and procedures are in place on how to handle sensitive data.
- Every data is marked as per the classification of the data.
- Necessary permissions are assigned based on the criticality of the data.
- Data Destruction
- We are following the NIST SP 800-88 Rev 1 “Guidelines for Media Sanitization”, which gives comprehensive, detailed sanitization info like clearing, pursuing and destroying. When the organization no longer needs sensitive data.
- Appropriate Data and Asset Retention Policies
- We define data retention policies based on the countries' laws and regulations.
- Software Development Security
- Zero Trust Cyber Security Architecture
- Development Security
- Follows the DevSecOps Development methodology.
- Follows Software Assurance Maturity Model.
- Follows OWASP recommended secure coding practices.
Experience the Power of Automated Security Testing