All Blogs
Automated Pentesting for SaaS: A CISO’s Blueprint for Continuous Security Assurance

Blog Overview: In the fast-moving SaaS world, traditional pentesting can’t keep up with continuous delivery and expanding attack surfaces. This blog explores why automated penetration testing has become a strategic necessity for CISOs — detailing its benefits, challenges, and best practices. Learn how continuous validation, attack path mapping, and DevSecOps integration redefine SaaS security.
The security mandate for today’s SaaS CISO has changed dramatically. The mission is no longer about preventing every breach; it’s about maintaining assurance at scale in an environment that never stops changing. When your organization deploys to production dozens of times a day, relies on hundreds of microservices, and integrates with countless third-party APIs, security validation can’t remain a quarterly ritual.
Traditional penetration testing still delivers value, especially for compliance, governance, and deep manual discovery. However, its cadence no longer aligns with the velocity of SaaS delivery. In practice, most CISOs find themselves relying on results that are already stalled by the time reports arrive. Attack surfaces evolve faster than audits can capture them.
That’s why many SaaS security leaders are rethinking their approach. Automated penetration testing has emerged as a strategic capability - one that complements human expertise by embedding continuous validation directly into DevSecOps workflows. The goal isn’t to replace human pentesting teams, but to ensure the organization maintains a permanent state of readiness.
The market shift reflects this urgency. Global penetration testing investments are projected to grow from $2.74 billion in 2023 to $6.25 billion by 2032, a sign that continuous validation is becoming operationally indispensable. At the same time, roughly 30% of enterprises now automate at least 70% of their security testing processes, underscoring a decisive move toward scale, consistency, and speed.
For CISOs leading SaaS organizations, this evolution is more than a technical shift. In fact, it’s a leadership challenge. The question is no longer if automation fits into your security strategy, but how effectively it can enhance visibility, trust, and resilience across your product lifecycle. This blog examines how, why, and with what caveats to adopt automated pentesting in SaaS environments.
Validate your security program with real-time exploit testing built for SaaS environments. Start Free Evaluation
On This Page
- Key Benefits of Automated Pentesting for SaaS Companies
- What is Automated Pentesting for SaaS Environments?
- Challenges and Limitations CISOs Should Know
- Embedding Pentesting into SaaS DevOps
- Attack Path Mapping and Business Logic Testing
- How to Evaluate Automated Pentesting Tools
- Best Practices for Automated Pentesting in SaaS
- Case Studies
- How ZeroThreat Can Help with Automated Pentesting
- Final Thoughts
Key Benefits of Automated Pentesting for SaaS Companies
Before diving into architecture, it’s worth establishing why automation matters for SaaS.
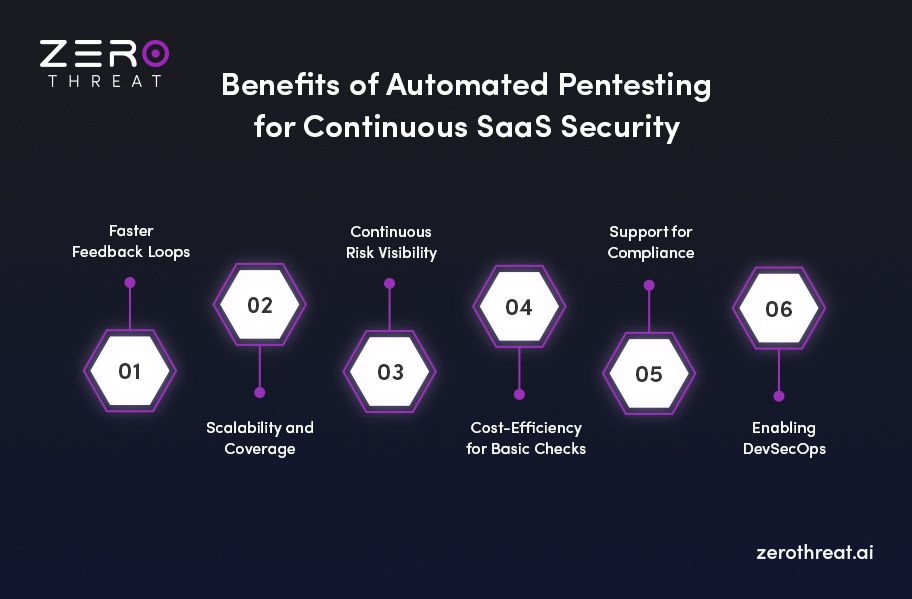
Faster Feedback Loops
Automated penetration testing can run on each build or deployment, reducing the “vulnerability window” between development and detection. Compared to quarterly or annual manual pentests, that can cut exposure time from months to hours or days.
Scalability and Coverage
SaaS CISO has several web apps, microservices, internal APIs, and third-party integrations, cloud infrastructure, service mesh, etc. And human teams alone can’t keep up with scale. Automation allows broad coverage of routine attack vectors and continuous scanning of evolving surfaces.
Continuous Risk Visibility
Automated penetration testing tools deliver real-time, continuous insight into your digital footprint. This helps you detect exposed assets and vulnerabilities before attackers can act. This proactive approach keeps your security posture current and minimizes hidden risks across your environment.
Cost-Efficiency for Basic Checks
Many of the “low-hanging fruit” vulnerabilities (e.g. missing headers, common misconfigurations, known CVEs) can be validated or even exploited by automation at lower cost than manual retests. Also, some free pentesting tools help you detect critical OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities as well.
Support for Compliance and Audit
Continuous or automated validation can be used to satisfy recurring control testing requirements (HIPAA, GDPR, SOC 2, ISO 27001, or internal audit) and to provide objective metrics to the board or auditors.
Enabling DevSecOps
Automated pentesting for SaaS CISOs pushes security earlier into the development life cycle (shift-left), catching issues before release rather than after. That reduces remediation burden and context-switching for dev teams.
What is Automated Pentesting for SaaS Environments?
Automated pentesting in SaaS uses software agents or orchestration engines to simulate attacker behaviors, identifying vulnerabilities.
An automated pentest engine typically:
- Performs reconnaissance/discovery (endpoints, services, API endpoints, cloud assets)
- Tests for known misconfigurations, weak credentials, CVE-based exploits
- Attempts to escalate privileges or exploit chained vulnerabilities
- Emulates attacker logic (e.g. pivoting, forwarding, lateral movement)
- Reports validated pathways (attack paths) and real exploitable findings
What to expect (and not expect) from automation
You can expect:
- Rapid detection of known misconfigurations (e.g. open buckets, missing headers, default credentials)
- Validated, chained exploit paths across known weaknesses
- Attack surface drift detection (changes, new endpoints)
- Metrics and dashboards for exploitation success rates, coverage, attack path likelihood
You should not expect:
- Deep business logic flaws (e.g. multi-step fraud chains, subtle race conditions)
- Creative novel zero-day exploit crafting
- Full context-aware threat modeling or adversary-level thinking
- Perfect precision — false positives or noise will exist
In short, automation is a force multiplier—but never a complete replacement for expert human pentesters.
Challenges and Limitations CISOs Should Know
When evaluating or adopting automated pentesting, CISOs must be keenly aware of pitfalls, trade-offs, and areas needing guardrails:
False Positives, Noise, and Alert Fatigue
Automated systems inevitably generate false positives. Without robust filtering, triage processes, and contextual tuning, your security team may drown in alerts. Ensuring that automation provides exploit-validated or path-validated findings is critical.
Environment Alignment and Context Mismatch
Running automated tests in staging environments may lead to mismatches relative to production of configs, data, and traffic. Some vulnerabilities only manifest under real data or load. Ensuring the testing environment mirrors production (in both infrastructure and data patterns) is nontrivial.
Risk of Causing Disruption
Aggressive exploit attempts can inadvertently cause crashes, service disruptions, degrade performance, or corrupt data. Boundaries must be set and rollback mechanisms must be prepared.
Credential Management and Isolation
Automated tools often need privileged credentials or service accounts. Managing those secrets securely and ensuring attack simulations don’t expose or misuse real credentials is essential. Use ephemeral or scoped credentials.
Regulatory/Compliance Limitations
Some compliance auditors may not accept only automated tests; they may insist on human-led pentesting or red-team validation for critical controls. Integration into compliance frameworks must be designed accordingly.
Scaling Readiness and Operational Load
Automated pentesting is not “set it and forget it.” It needs ongoing tuning, false-positive filtering, resource management, and coordination with development and operations. Inadequate staffing or process of maturity may undermine benefits.
Empower your security team with data-driven validation and compliance-ready reporting. Leverage Pentesting Tool
Continuous Assurance: Embedding Pentesting into SaaS DevOps
To derive maximum value, automated pentesting must be integrated into the DevSecOps pipeline rather than being a separate, after-the-fact activity.
1) Architecture for Pipeline Integration
- Asset Discovery and Configuration Sync: Use Infrastructure-as-Code (IaC), service catalog, or asset management to feed the automation engine a live inventory of endpoints, APIs, domains, microservices, and dependencies before each test.
- Pre-Deployment Checks (Staging): Run lightweight automated pentests in the staging environment as part of the build pipeline, catching regressions or new exposures before they hit production.
- Post-Deployment: After deployment, automatically trigger a scan in production-lite or shadow mode to catch drift or unexpected exposures.
- Feedback Loops & Gating: Fail builds or deployments based on risk thresholds (e.g. exploit path score > threshold), or require manual review for high-risk findings.
- Remediation & Retest Automation: Findings should produce tickets (Jira, GitHub, etc.) automatically. Upon fixing, re-execute the test (or relevant segments) to validate resolution.
- Dashboarding, Audit Logs & Metrics: Maintain a central dashboard with trends (exploit rate, path length, recurring issues) and audit logs to support incident reviews, compliance, or board reporting.
2) Organizational alignment
- DevSecOps Culture: Embed security as part of “you build it, you own it.” Teams must accept security feedback earlier, rather than as a “bolt-on” after development.
- SLA/Remediation Binding: Agree SLAs for issue resolution (critical/high/medium). Automated pentesting amplifies the flow of findings—without remediation discipline, the queue grows.
- Security Champions: Designate engineers or architects in each team to help triage, interpret automation outputs, and drive fixes.
- Training & Playbooks: Provide engineers with context and remediation guidance, so automation findings don’t feel like black-box errors.
- Periodic Manual Review: Augment the automation baseline with human-led deep tests (especially for new feature launches or logic flows).
By embedding automation within the DevOps lifecycle, a SaaS CISO can shift from “point-in-time audits” to continuous assurance.
Targeted Value: Attack Path Mapping and Business Logic Testing
Automation is not only about surfacing discrete vulnerabilities but also mapping them into attack paths and validating business logic risk.
Attack Path Mapping
Automated pentesting tools for SaaS CISOs should analyze chains of exploitable weaknesses to build a graph of possible paths from initial access to critical resources. This gives you:
- Contextual Risk: We all know that not all vulnerabilities are equally risky. Path-based scoring helps you focus on issues that lead to sensitive data or privilege escalation.
- Exploitability Insight: You see which vulnerabilities are exploitable in sequence, not just in isolation.
- Remediation Prioritization: Fixing a node early in an attack path can block multiple downstream paths.
- Trend Detection: If new versions shorten path lengths or open new pivots, you get alerted.
As an example, an automated pentest might chain: API endpoint misconfiguration → weak JWT signing key → token forgery → privilege escalation → access to admin APIs. You then know which intermediate step is the real bottleneck to remediate.
Business Logic
Even though automation struggles with deeply creative business logic flaws, the frontier is shifting: newer frameworks integrate scenario-based logic models to simulate workflows (e.g. “transfer money between accounts,” “escalate settings via nested API calls”).
While not perfect, these can help detect obvious logic abuses (e.g. missing authorization on a “bank-to-bank transfer,” or parameter tampering). Advanced automation may feed multiple transaction permutations into API chains and test for abnormal state changes.
As these frameworks mature, they will become a critical bridge between pure vulnerability exploitation and real-world business impact testing.
CISO Decision Guide: How to Evaluate Automated Pentesting Tools
Selecting an automated pentesting platform isn’t only about features or capabilities; it’s also about fit, transparency, and control. The right security testing tool for CISOs should extend your existing security strategy, not complicate it. When evaluating options, CISOs should focus on six essential dimensions:
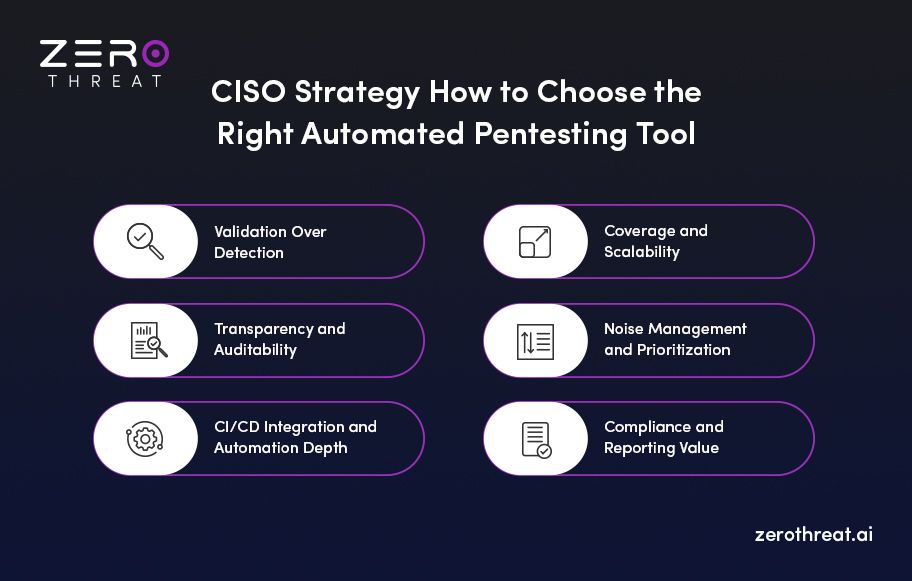
1) Validation Over Detection
Prioritize platforms that prove exploitability but not just flag potential CVEs. Look for verified attack paths, replayable evidence, and context-rich findings that tie directly to business risk.
2) Transparency and Auditability
Avoid black-box tools. Insist on step-by-step exploit logs, chain logic visibility, and clear mapping between vulnerabilities, assets, and exposure pathways.
3) CI/CD Integration and Automation Depth
Ensure seamless alignment with your DevSecOps ecosystem — GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Jenkins, etc. Testing should trigger automatically and report findings where developers already work.
4) Coverage and Scalability
Assess how well the tool handles multi-tenant SaaS architectures, including web apps, APIs, and cloud assets. Continuous discovery of new attack surfaces is a must.
5) Noise Management and Prioritization
A mature solution filters false positives and ranks findings by exploitability, attack path depth, and data sensitivity.
6) Compliance and Reporting Value
The best tools produce evidence ready for SOC 2, HIPAA, PCI DSS, or internal audits, complete with remediation tracking and trend metrics.
Best Practices for Automated Pentesting in SaaS
To increase success and minimize risk, here are the best practices every CISO should adopt for automated pentesting in SaaS organization:
Start Controlled, Then Scale
Begin with non-critical apps or staging environments. Tune thresholds, watch for noise, and validate exploit evidence before expanding coverage.
Integrate, Don’t Isolate
Treat automated pentesting as part of your DevSecOps workflow — not a side project. Findings should flow into the same CI/CD, ticketing, and remediation pipelines developers already use.
Prioritize Actionable Results
Filter out noise. Focus on exploit-validated issues mapped to business risk and asset sensitivity. Automation should clarify, not overwhelmed.
Keep a Human Layer
Pair automation with periodic manual reviews to cover logic flaws and unknown attack paths. Automation scales coverage, and humans add depth.
Govern with Metrics
Track key indicators like mean-time-to-remediate, recurring vulnerabilities, and exploit path trends. Use these as measurable KPIs for board-level reporting.
Continuous Improvement Loop
Refine automation over time, feedbacks on false positives, adjust thresholds, and evolve custom logic modules as your SaaS product changes.
Strengthen your SaaS security strategy with automated pentesting insights tailored for CISOs. Contact Our Security Team
Case Studies: SaaS Companies Succeeding with Automated Pentesting
Here are two representative examples explaining how automation transformed security programs in SaaS companies.
Case Study A: “CloudMetrics”: SaaS analytics platform
Challenge: Frequent releases, complex microservice architecture, multiple customer integrations, and growing complaints from dev teams about pentest bottlenecks. Manual pentests happened quarterly and often missed drifts.
Approach:
- CloudMetrics introduced an automated pentesting engine in staging and production-lite shadow mode.
- They gated builds only when exploit path scores exceeded thresholds.
- Dev teams were trained to triage findings, and a security champion in each team handled validation.
- Occasional manual deep dives focused on newly launched modules.
Result:
- Exploitable issues discovered within hours of deployment rather than months later.
- The number of critical vulnerabilities reaching production dropped by 70%.
- Developer friction decreased because findings arrived earlier and with better context.
- The security team shifted from firefighting to proactive risk management.
Case Study B: “FinSaaSPro”: Financial SaaS for Payments
Challenge: Handling sensitive financial transactions and compliance (PCI DSS) requires high assurance and regular pentesting. The release cadence was aggressive.
Approach:
- They built a “validation pipeline” where each major API change triggered an automated pentest plus a narrow manual review.
- Attack path results were mapped to a risk scoring engine, which determined whether further manual review was mandatory.
- They pushed remediations and retests into the same pipeline, closing the loop quickly.
- External auditors accepted the automation logs combined with periodic manual audits to satisfy compliance.
Result:
- The security team avoided overdependence on external pentest firms, cutting pentest cost by 30% yearly.
- Time between vulnerability detection and remediation dropped from weeks to 48 hours on average.
- Audit cycles became smoother because proof of artifacts (logs, exploit chains, retest results) were always available.
How ZeroThreat Can Help SaaS CISO with Automated Pentesting
ZeroThreat enables SaaS CISOs to leverage continuous penetration testing. Its AI-driven engine continuously maps vulnerabilities, attack paths, and misconfigurations across web apps and APIs, validating each exploit in real time.
By integrating security testing directly into CI/CD pipelines, ZeroThreat helps security teams:
- Automate exploit validation within every release cycle. This reduces detection-to-remediation time from weeks to hours.
- Visualize attack paths that show exactly how a threat could move from exposure to impact.
- Align findings with compliance frameworks like PCI DSS and HIPAA, simplifying audit readiness.
- Empower developers and security engineers with contextual, remediation-ready insights instead of static vulnerability reports.
In a nutshell, ZeroThreat bridges the gap between continuous delivery and continuous assurance, giving CISOs confidence that every deployment is tested, validated, and audit-ready by design.
Still not convinced? Try ZeroThreat free and see why more than 3,000 organizations trust it to secure their SaaS applications.
Final Thoughts
Automated pentesting for SaaS CISOs is no longer optional, it’s a strategic necessity to keep pace with modern development speed, scale, and threat sophistication. As attack surfaces expand and release cycles accelerate, security validation must match that speed continuously.
The real value of automation isn’t in replacing humans, but in extending their reach. When integrated into DevSecOps pipelines, it transforms pentesting from a reactive event into an ongoing assurance process, one that validates every release, every change, and every exposed endpoint.
The future of SaaS security will be defined by this balance: automation for scale, human expertise for depth, and governance for trust.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the biggest compliance risks for SaaS CISOs if pentesting isn’t conducted regularly?
Irregular pentesting leaves CISOs exposed to undetected vulnerabilities that violate SOC 2, ISO 27001, or PCI DSS controls. Gaps in validation can result in data exposure, audit failure, and loss of customer trust.
Are automated pentesting tools effective for uncovering cross-tenant data leaks?
What role does AI play in the future of automated pentesting?
Are there risks of false positives with automated pentesting tools?
What’s the difference between PTaaS (Pentesting-as-a-Service) and automated pentesting platforms?
How can SaaS CISOs ensure pentesting results are actionable and easily adopted by developers?
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


