All Blogs

Quick Summary: SSL hijacking is one of the many cyberattack tactics that attackers leverage to steal data or infect the target system with malware. It can cause severe damage if the attack is successful. Keep reading to learn more about this attack vector in this blog and ways to prevent it.
Secure connection over the internet is paramount. And SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) is the backbone of a secure connection between a web browser and a server. But what if an attacker places himself between this browser-server interaction and intercepts the sensitive data? SSL hijacking is the attack vector that causes such a security issue as it allows an attacker to use a fake SSL to interrupt normal user-server communication and get in the middle of this interaction.
In fact, attackers achieve this by exploiting weaknesses in SSL/TLS protocols, using various techniques like Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attacks, rouge certificates, and session hijacking. This way, they can gain access to sensitive data and cause dozens of other security issues.
Therefore, it is essential to understand SSL hijacking and proactive methods to mitigate its risk. Whether you are a business securing customer data or an individual protecting your online transactions, knowing various methods for SSL hijacking prevention is essential.
Let’s read what is SSL hijacking and tips to prevent it in this given blog.
Protect Your Data from Hidden Security Threats with 98.9% Precision Uncover Lurking Threats
On This Page
- What is SSL Hijacking?
- How Does SSL Connection Work?
- How Does SSL Hijacking Work?
- How to Detect SSL Hijacking?
- Types of SSL Hijacking Attacks
- What are the Business Risks of SSL Stripping Attacks?
- How to Prevent SSL Hijacking Attacks?
- How ZeroThreat Helps with SSL Hijacking Prevention?
- Protect Your Assets Against SSL Hijacking Attacks
What is SSL Hijacking?
SSL hijacking, known as SSL Striping, is a cyberattack tactic in which an attacker can eavesdrop on communication between a web browser and a server. This enables them to downgrade the secure HTTPS connection to an unencrypted HTTP connection.
During SSL attack, the attacker uses a fake SSL certificate to trick victims into believing that they are connecting to a secure website, but they actually don’t.
In reality, they connect to a proxy or cloned site, which is apparently controlled by the attacker. SSL hijacking is a kind of Man-in-the-Middle (MITM) attack technique. So, just like the MITM, the attacker gets into the middle of a legitimate site and the victim.
So, what happens here is that whenever a victim tries to visit a legitimate site, the connection request goes to the attacker instead. Additionally, the information provided by the victim passes through the attacker to the legitimate site. This enables the attacker to intercept the communication.
There are many dire consequences of a successful SSL attack, like the attacker can access sensitive data. For example, you send a decoded message to a recipient. Since the message is decoded, you assume that it is secure because only the recipient knows how to decode it.
However, an attacker can intercept and decipher this message with SSL hijacking. The attacker can decode the message and get credentials to gain unauthorized access to your data.
How Does SSL Connection Work?
Imagine you are logging into your bank’s website, which is more secure because of that little padlock icon in your browser. This means, SSL/TLS (Secure Socket Layer/Transport Layer Security) is working hard to encrypt your data, which ensures your sensitive information – passwords and financial details remain private.
But what if an attacker could slip into that secure connection, intercept your data, and even manipulate the information being exchanged? That’s what SSL hijacking is.
SSL/TLS is the gold standard for securing web traffic, which protects everything from online banking to business communications.
How Does SSL Hijacking Work?
Now we have a clear understanding of what an SSL attack is, but how does it occur in reality? Well, this attack isn’t feasible directly because web browsers are configured to trust SSL certificates that are signed by a trusted certificate authority.
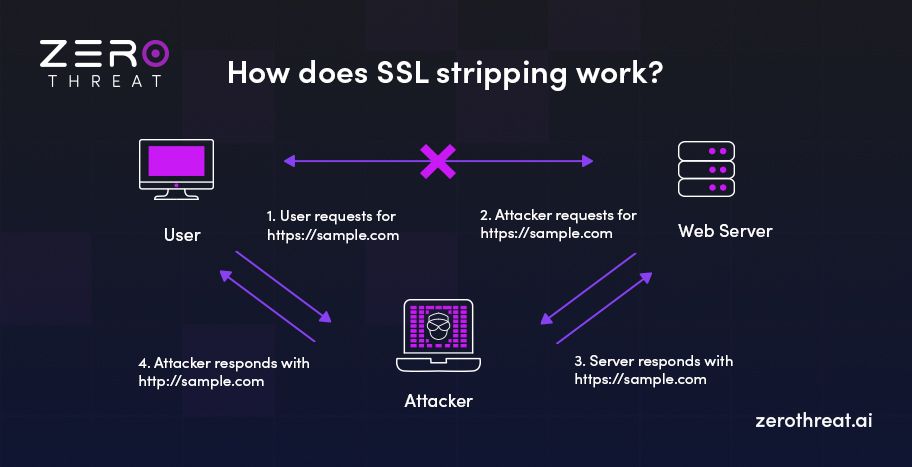
In this case, an attacker needs to combine multiple tactics to achieve the objective. The attacker starts by adding another certificate authority to the default ones preconfigured in operating systems like Windows and Linux using phishing or exploiting vulnerabilities.
However, even if an attacker is unable to add an SSL certificate, they can use the SSL stripping technique to force a victim’s web browser to use HTTP instead of HTTPS. In that case, the victim’s browser easily connects to an unsecured network without any complaint.
Once an attacker generates an SSL certificate, your browser will not throw any warnings. Well, the reason why the browser doesn’t show warnings is simple, the attacker has successfully added the certificate authority (CA) and now the browser considers the fake SSL as valid.
However, there is another task for the attacker before launching the SSL attack. The attack takes place by replacing the IP of the domain a user intends to visit with the IP of the attacker. With the use of attack methods like DNS spoofing or DNS cache poisoning, the attacker overwrites the cache records that redirect users to the intended website.
After these adjustments, the playfield is ready for the attacker, and they carry out the SSL hijacking attack in the following steps.
- The attacker tricks a victim user into downloading a fake SSL that will be accepted by the victim’s web browser without any warning.
- The attacker sets up a web server as a proxy that will accept any requests sent to a server that a user intends to use, like example.com. So, the proxy will accept requests, such as those from example.com.
- Due to manipulation in the DNS records on the victim’s system, the browser connects to the attacker's server whenever the victim hits www.example.com in the address bar.
- When the browser establishes a connection with the attacker’s server, it receives the fake SSL and verifies it based on the CA added by the attacker.
- After this, there is an encrypted connection between the victim’s browser and the attacker’s server. Moreover, the attacker decrypts the information and forwards it to the correct “example.com” domain. So, the attacker can now intercept the information.
- The attacker creates two separate connections – one is between the victim’s browser and the attacker’s server and the second one is between the attacker’s server and the example.com’s server.
- So, now it is an SSL hijacking attack. It allows the attacker to steal sensitive data like credit card information, login credentials, and more. Additionally, the attacker can also perform other SSL striping attacks like session hijacking.
How to Detect SSL Hijacking?
SSL hijacking is a tricky attack that is not easy to detect. As a matter of fact, a targeted web server has no way to know if the connection request is coming from a legitimate user or an attacker. On the other hand, if the fake SSL hasn’t been installed on the victim’s system, the browser will throw a warning of an invalid certificate.
However, if the SSL has been installed, it becomes difficult to detect SSL threats. So, there are some challenges in identifying this deceptive attack. Fortunately, there are also a few signs and tools that can help detect this attack vector to protect sensitive information.
The first line of defense against the SSL risk is cybersecurity awareness. It applies to both the common users and the employees of an organization. Attackers leverage social engineering techniques to trick victims into installing fake SSL certificates.
Cybersecurity awareness helps users and employees avoid falling prey to these threats. There are many signs like “Certificate invalid” and “Your connection is not private” that browsers produce, and users should be cautious after seeing such signs.
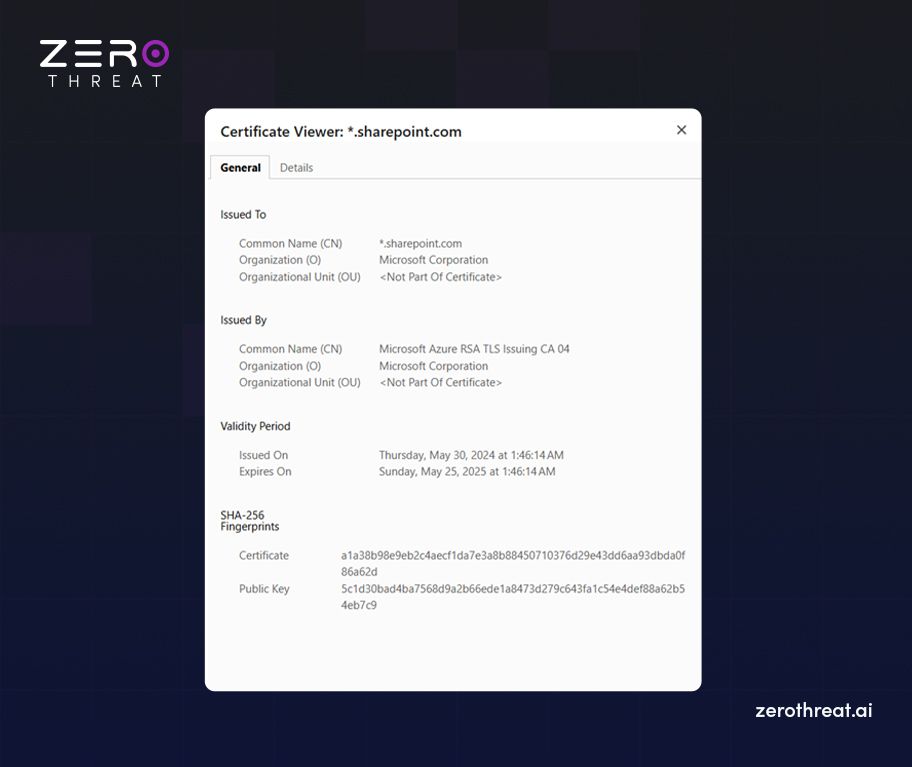
Users can check certificate information from their web browsers to get details like the expiration date, the authority that issued the certificate, the domain for which the certificate is issued, etc. The following image shows an example of a real-life SSL certificate.
Using network monitoring tools can also help identify SSL hijacking. These tools help detect suspicious activities like abrupt fluctuations in network traffic, connection requests from untrusted IP addresses, and more.
Secure Your Digital Assets by Uncovering Vulnerabilities with AI-powered Threat Detection Start Now
Types of SSL Hijacking Attacks
When an SSL striping attack occurs, it becomes challenging for an attacker to perform the man-in-the-middle attack to intercept traffic between the server and the client. And this can be achieved in several ways, including:
ARP Spoofing
ARP Spoofing is performed when an attacker is on the same local area network (LAN) as the target. This attack maps the target’s IP address to attacker’s MAC address. As a result, all data meant for the intended recipient is redirected to the attacker’s system instead.
Proxy Servers
In a proxy server attack, a computer is configured to use a proxy server. This causes all traffic to be sent to a particular location en route to its destination. If an attacker tricks a target’s computer into using their server as a proxy, they can intercept and analyze all of the user’s browsing traffic.
Malicious Public Wi-Fi
An attacker can create a fake public Wi-Fi network that looks like a trusted one. When users connect, the attacker can intercept and monitor all wireless traffic passing through their malicious router.
What are the Business Risks of SSL Stripping Attacks?
SSL stripping attacks eliminate the protection provided to web traffic using SSL/TLS. This can lead to several serious business risks, such as:
Sensitive Data Leakage: SSL stripping allows an attacker to decrypt and read all data between the client and the server. This leads to exposure to sensitive information.
Credential Theft: SSL hijacking attacks allow attackers to capture personal information and credentials by entering them into their unencrypted websites using various tricks.
Phishing and Fraud: An attacker may serve a malicious version of a website, which can redirect them to fake websites or phishing pages. As a result, they can capture additional information upon users revealing more data.
Data Manipulation: Attackers utilize various tactics to inject malicious content and modify responses from the website. This way, they can manipulate data easily.
Loss of Trust and Reputation Damage: Successful attacks can not only steal sensitive information, but they can also damage your organization’s reputation. Eventually, it leads to a loss of user trust and confidence in your brand.
Compliance Violations: Sensitive data leakages may lead to violation of data protection regulations. This results in legal consequences and financial penalties.
How to Prevent SSL Hijacking Attacks?
Once the hijacking of SSL occurs, it becomes difficult to track it. So, it is wise to focus on preventing this threat. There are different measures that can help prevent it, as given below.
Use HSTS
It is an effective browser policy mechanism that can help defend against downgrade attacks. HSTS (HTTP Strict Transport Security) helps prevent the redirection of secure HTTPS connections to an attacker-controlled server. It prevents bypassing SSL warnings. It also transforms insecure HTTP links into secure HTTPS.
Browser Updates
Keeping the web browser up to date can also help tackle many cybersecurity issues. Typically, attackers take advantage of the SSL vulnerability to redirect users to a malicious site. Weak security policies in outdated browsers are conducive to hijacking attacks.
Stay Alert for Phishing
Phishing is a deceptive technique that attackers frequently use to deliver malware, fake SSL/TLS certificates, malicious links, and more. So, it is crucial to be careful of unsolicited or suspicious emails. Users must stay careful with any attachments or links to these emails as they could lead to the hijacking of their SSL session.
Avoid Using Public Wi-Fi
Attackers often exploit public Wi-Fi to steal sensitive data from users connected to it. Usually, these networks lack robust security measures, which makes them susceptible to hacking. Hence, when users connect to these networks, attackers can access their information easily as there is no security.
How ZeroThreat Helps with SSL Hijacking Prevention?
As we know, SSL hijacking is a real threat to your application. Choosing the right security testing tool, ZeroThreat, helps you prevent it. With its AI-powered security testing and threat detection, ZeroThreat provides a multi-layered defense against such attacks.
Let’s understand how:
1. Advanced SSL/TLS Configuration Analysis
ZeroThreat scans SSL/TLS configurations to identify vulnerabilities such as:
- Outdated or misconfigured certificates that leave connections open to MITM attacks.
- Weak cipher suites that attackers exploit to downgrade encryption.
- SSL striping vulnerabilities, where attacker forces move to HTTP from HTTPS.
2. Active MITM Attack Detection
ZeroThreat monitors and detects anomalies indicative of MITM attacks, such as:
- Inconsistent encryption levels during session negotiation.
- Unexpected SSL/TLS certificate changes, which may indicate a rogue certificate injection.
3. Enforcing HTTPS and HSTS Policies
By analyzing your web app and APIs, ZeroThreat ensures your apps enforce HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS). This helps you create an encrypted connection, preventing SSL stripping attacks. It also checks for mixed content vulnerabilities, where secure pages load insecure resources, creating an entry point for attackers.
4. AI-Driven Threat Intelligence and Alerts
With AI-driven threat intelligence, ZeroThreat monitors SSL/TLS patterns and flags any suspicious activity. If it finds any unauthorized SSL proxy or rouge access point, it displays remediation actions to prevent session hijacking.
Strengthen Your Security Shield to Thwart Cyberattacks by Identifying Loopholes Discover Risks Now
Protect Your Assets Against SSL Hijacking Attacks
Man-in-the-middle attacks like SSL hijacking are a critical security challenge for organizations and their users. They allow attackers to steal sensitive data like credit card details, login credentials, session tokens, and more.
Cybersecurity awareness plays a vital role in protecting against such threats. Besides, organizations should also take additional measures to make sure that users can securely connect with their servers.
Organizations can ensure secure connections between their servers and users by tackling security issues like misconfigurations, broken authentication, weak access controls, and more. However, it requires continuous security audits to identify security weaknesses.
ZeroThreat is a powerful tool for vulnerability scanning that helps uncover thousands of CVEs, allowing organizations to strengthen their security posture. It has an AI-powered spider that can detect vulnerabilities with 98.9% accuracy.
Scan with ZeroThreat to prevent SSL hijacking now.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the dangers of SSL hijacking?
Well, in reality, this is quite a dangerous threat vector. However, an attacker needs to combine many techniques like IP spoofing and DNS cache poisoning to carry out this attack, which makes it a bit difficult. Nevertheless, once successful, an attacker can access sensitive data or redirect the victims to a malicious site.
What does an SSL vulnerability mean?
What does SSL spoofing mean?
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


