All Blogs
From CVEs to Zero-Days: Cybersecurity Vulnerability Statistics

Quick Overview: This blog explores the latest cybersecurity vulnerability statistics for 2025, uncovering the surge in CVEs, rapid exploit rates, and AI-powered threats. It highlights key trends, industry-specific risks, and actionable insights to help security teams stay ahead in an increasingly complex and fast-moving threat landscape.
2025 is turning out to be a turning point in the cybersecurity industry. With digital transformation accelerating and artificial intelligence reshaping how we build and break systems, the number and severity of vulnerabilities are surging at an unprecedented pace.
The cybersecurity community is facing not just a numbers game, but a complexity crisis: vulnerabilities like CSRF, SQLi, and XSS are no longer isolated software bugs; they are critical business risks, frequently exploited in minutes rather than months.
This in-depth report delivers a research-backed, data-rich analysis of the most significant vulnerability trends of 2025—from CVE volumes to zero-day exploitations, from AI-driven scanning to sector-specific threats. Whether you’re a security engineer, a CISO, or a DevSecOps lead, this research will help you understand how the threat landscape has shifted, and how to prioritize your next move.
Cyber Threats are Getting More Elusive and Riskier, ZeroThreat Offers Laser-Focused Assessment to Hunt Them All! Check Our Pricing List
On This Page
- The Vulnerability Surge in 2025
- Vulnerability Intelligence Update – As of June 2025
- Cybersecurity Vulnerability Statistics in 2025
- Most Vulnerable Industries in 2025
- Top Vulnerable OSS Libraries
- Top Countries Producing Vulnerable Code
- Important Cyber Security Vulnerabilities Statistics 2025
- Detection and Severity of Vulnerabilities
- Critical Application Security and Threat Exposure Stats
- Final Thoughts: From Awareness to Action
The Vulnerability Surge in 2025
As of June 2025, a staggering 21,528 vulnerabilities have already been published, marking an 18% increase compared to the same period last year.

- Average vulnerabilities reported per day: 133
- Year-over-Year increase in total vulnerabilities: +3,285
That’s 133 new vulnerabilities every single day that security teams must detect, assess, and patch—across thousands of devices and applications.
Vulnerability Severity Breakdown
| Severity Level | Count |
|---|---|
| Critical | 1,773 |
| High | 6,521 |
| Medium | 10,607 |
| Low | 582 |
| Unrated | 2,040 |
Over 38% of reported vulnerabilities fall under critical or high severity, demanding immediate attention and risk mitigation.
What This Means for Your Organization
With 133 new cybersecurity vulnerabilities surfacing each day in 2025, organizations face relentless pressure to:
- Identify and prioritize critical risks
- Patch systems across complex, distributed IT environments
- Maintain compliance with evolving security standards
Manual tracking simply can’t keep up.
According to recent reports, January 2025 recorded the highest number of published CVE vulnerabilities so far this year, with a total of 4,278 vulnerabilities disclosed.
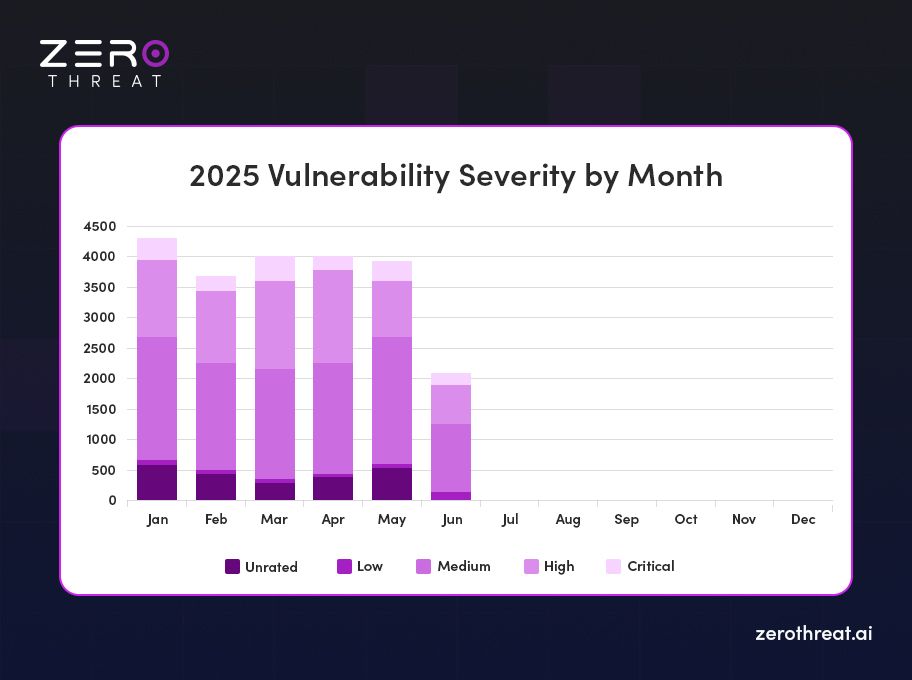
| Month (2025) | Total Vulnerabilities | Critical | High | Medium | Low | Unrated |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| January | 4,278 | 304 | 1,300 | 2,024 | 80 | 570 |
| February | 3,677 | 270 | 1,087 | 1,791 | 119 | 410 |
| March | 4,015 | 403 | 1,331 | 1,966 | 111 | 204 |
| April | 4,036 | 341 | 1,355 | 1,886 | 121 | 333 |
| May | 3,984 | 366 | 1,013 | 1,987 | 117 | 501 |
Insight: Over 38% of January’s vulnerabilities were classified as high or critical, posing significant risk to organizations across sectors.
This spike underscores the urgent need for automated pentesting, vulnerability assessment, and monitoring to stay ahead of the evolving threat landscape.
Vulnerability Intelligence Update – As of June 2025
Staying ahead of the threat curve requires real-time awareness of CVEs (Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures) and how they’re evolving. Here’s a snapshot of the most recent data from global CVE vulnerability databases:
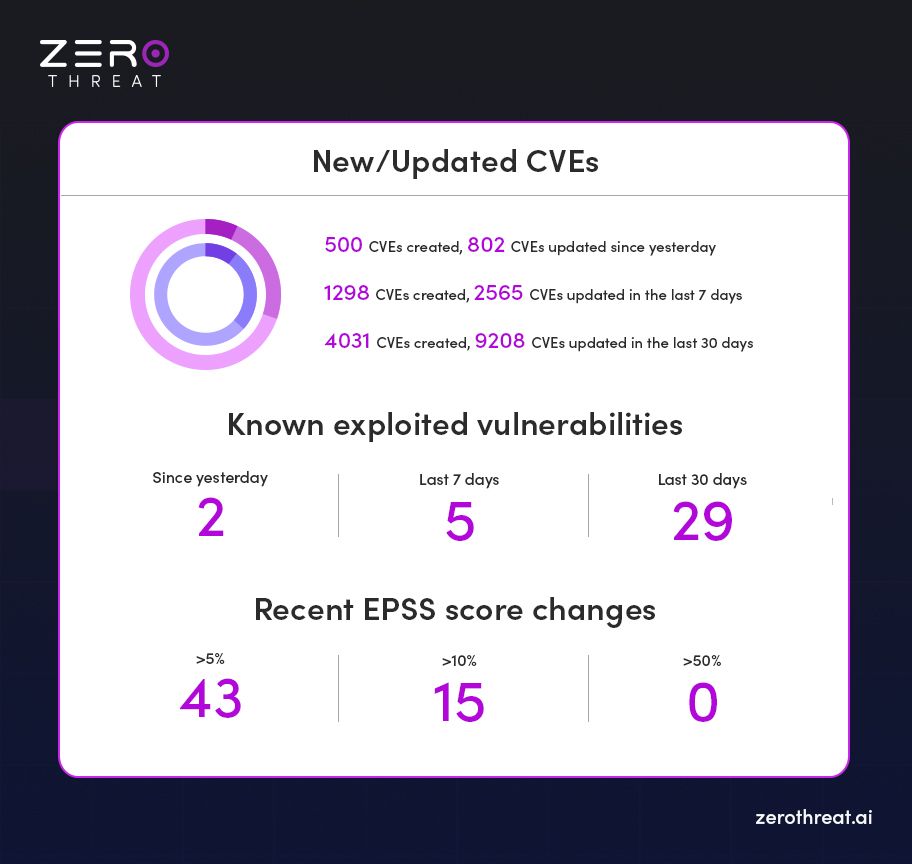
CVE Activity Overview
- In the Last 24 Hours:
- 500 new CVEs created
- 802 existing CVEs updated
- In the Last 7 Days:
- 1,298 new CVEs created
- 2,565 CVEs updated
- In the Last 30 Days:
- 4,031 new CVEs created
- 9,208 CVEs updated
Insight: With over 4,000 new vulnerabilities in just a month, threat actors are gaining a wider attack surface—forcing security teams to scale detection, prioritization, and remediation rapidly.
Known Exploited Vulnerabilities
The U.S. Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA) and other global feeds have confirmed:
- Exploited in the Last 24 Hours: 2 CVEs
- Exploited in the Last 7 Days: 5 CVEs
- Exploited in the Last 30 Days: 29 CVEs
EPSS (Exploit Prediction Scoring System) Updates
The Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS) helps predict the likelihood a CVE will be exploited in the wild. Over the past day:
- 43 CVEs saw a >5% increase in EPSS score
- 15 CVEs jumped by more than 10%
- 0 CVEs showed a >50% score spike
Experience Advanced DAST Scanning with Zero Setup and Secure Your Apps Start Scanning Now
Cybersecurity Vulnerability Statistics in 2025: Key Takeaway
Year 2024 experienced a wave of critical vulnerabilities, starting with a major flaw in Chromium-based browsers. From Follina to Log4Shell, several high-impact vulnerabilities kept security teams and business leaders on high alert.
Certainly! Here's a polished rewrite of both vulnerability descriptions, suitable for a blog or report:
Microsoft SharePoint – RCE via Deserialization (CVE-2024-38094)
A serious deserialization flaw in Microsoft SharePoint allows attackers to perform remote code execution (RCE). Actively exploited and listed in CISA’s Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, it underscores the pressing need for immediate patching and risk mitigation.
Impact: Threat actors can remotely execute malicious commands, potentially compromising internal systems and sensitive data within enterprise environments.
Grafana – SQL Expression Injection (CVE-2024-9264)
Over 100,000 Grafana instances, including nearly 19,000 in the U.S., are vulnerable. Exploiting SQL expressions, attackers can execute commands and access restricted files—even with just Viewer permissions.
Impact: Exploitable in critical systems relying on CUPS, especially across Red Hat, Debian, and other Unix-based servers, risking full system compromise.
CUPS – Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities (CVE-2024-47176, CVE-2024-47076)
Multiple vulnerabilities in the Common Unix Printing System expose over 300,000 devices globally to RCE attacks. Affects major Linux distributions including Debian, Red Hat, and macOS, highlighting a wide threat surface in Unix-based environments.
Impact: Exploitable in critical systems relying on CUPS, especially across Red Hat, Debian, and other Unix-based servers, risking full system compromise.
Ivanti Cloud Services Appliance – OS Command Injection (CVE-2024-8190)
Discovered in September 2024, this flaw enables attackers with admin access to execute remote commands. Affected versions (CSA 4.6 Patch 518 or earlier) must be patched urgently to prevent privilege misuse.
Impact: High-risk for enterprises using Ivanti for remote infrastructure; attackers can seize full control with elevated privileges.
Apache OFBiz – Pre-Authentication RCE (CVE-2024-38856)
This pre-auth vulnerability allows unauthenticated attackers to run arbitrary code in Apache OFBiz. It continues to be a high-value target, reinforcing the importance of version upgrades and secure defaults.
Impact: Can lead to full server takeover; exploited in the wild due to its ease of execution on outdated OFBiz deployments.
OAuth Implementation Flaw – Leading to Widespread XSS
A misconfigured OAuth implementation affects millions of websites, exposing them to cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks. The issue underlines the need for strict validation and hardened auth logic in web applications.
Impact: Identity theft, unauthorized data access, and risk of full account compromise for websites lacking input validation.
ServiceNow – Critical Exploits (CVE-2024-4879, CVE-2024-5217)
Exploited flaws in ServiceNow’s ITSM platform led to breaches of over 105 databases. With CVSS scores of 9.3 and 9.2, the data was sold on dark web forums for up to $5,000 per set.
Impact: Exposed customer records were reportedly sold for $5,000 per database on dark web forums, endangering enterprise integrity.
Apache OFBiz – Authentication Bypass (CVE-2023-51467)
This vulnerability persisted despite a previous patch (CVE-2023-49070), allowing attackers to bypass authentication. It highlights the risks of incomplete fixes and the need for root-cause resolution.
Impact: Demonstrates the risk of incomplete fixes; allows adversaries unauthorized access to enterprise resource planning systems.
LiteSpeed Cache (WordPress Plug-in) – Critical XSS Flaw
Disclosed in July 2024, this vulnerability affects over 6 million WordPress installations. It allows unauthenticated attackers to inject code, escalate privileges, and steal sensitive data with a single HTTP request.
Impact: Enables site takeover, data theft, and malicious payload injection into popular WordPress-powered websites.
GOAnywhere MFT – Admin Creation Exploit (CVE-2024-0204)
A critical flaw in Fortra’s MFT platform enabled attackers to create admin accounts and gain full control of systems. Versions prior to 7.4.1 were affected, leading to potential mass data breaches.
Impact: Leads to total compromise of file transfer systems, with breach potential across banking, healthcare, and government sectors.
MOVEit MFT Breach – CLOP Ransomware Campaign
The MOVEit vulnerability exploited by CLOP ransomware exposed over 77 million records across 2,600+ organizations. Damages exceeded $12 billion, affecting entities like the U.S. Department of Energy.
Impact: Damages exceeded $12 billion, with critical institutions like the U.S. Department of Energy impacted, making this one of 2024’s most devastating breaches.
Black Basta – Windows Privilege Escalation (CVE-2024-26169)
Used by the Black Basta group, this vulnerability enabled elevation of privilege on unpatched Windows systems. Despite a patch issued in March 2024, delayed updates left many exposed.
Impact: Despite patches, slow adoption led to widespread infections, reinforcing the urgency of timely security updates.
TellYouThePass Ransomware – PHP Exploit (CVE-2024-4577)
This campaign exploited a PHP flaw in default XAMPP stacks on Windows, targeting public IPs with ransomware. Victims were hit with demands of 0.1 BTC (~$6,000) per infection.
Impact: Victims faced ransom demands of 0.1 BTC (~$6,000), with small-to-midsize enterprises most vulnerable due to default configurations.
Stay Abreast of Hackers with Pinpoint Vulnerability Detection in Apps in Apps and Early Remediation Before Launching to Productionchinching to Production Let’s Get Started
Most Vulnerable Industries in 2025
| Industry | No of Vulnerabilities | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| Software Development | 6,432 | 22.4% |
| Networking & Telecommunications | 4,876 | 17.0% |
| Consumer Electronics | 3,201 | 11.1% |
| Healthcare | 2,894 | 10.1% |
| Industrial Control Systems (ICS) | 2,108 | 7.3% |
| Finance | 1,987 | 6.9% |
| Government | 1,652 | 5.8% |
| Automotive | 1,432 | 5.0% |
| Education | 1,243 | 4.3% |
| Retail & E-commerce | 1,119 | 3.9% |
- Software development remains the most vulnerable sector, driven by the rapid release cycles of open-source libraries and cloud-native tools.
- Healthcare saw a 14.6% increase in vulnerabilities compared to 2024, raising concerns about patient safety and medical device security.
Top Vulnerable OSS Libraries
Supply chain attacks targeting OSS components increased by 22% in 2025, including notable incidents involving malicious npm packages and compromised PyPI modules.
| Library | No of Vulnerabilities | Critical Index |
|---|---|---|
| OpenSSL | 214 | High |
| jQuery | 189 | Medium |
| Apache Struts | 178 | High |
| FFmpeg | 167 | Medium |
| Linux Kernel | 156 | High |
| TensorFlow | 143 | Medium |
| WordPress Plugins | 139 | Medium |
| Python Packages (PyPI) | 132 | Medium |
| Node.js Modules | 128 | Medium |
| Android SDK | 121 | High |
Top Countries Producing Vulnerable Code
| Country | No of Vulnerabilities | % of Total |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 9,321 | 32.4% |
| China | 4,209 | 14.6% |
| Germany | 2,104 | 7.3% |
| India | 1,987 | 6.9% |
| Japan | 1,762 | 6.1% |
| South Korea | 1,432 | 5.0% |
| Canada | 1,223 | 4.3% |
| United Kingdom | 1,112 | 3.9% |
| Russia | 987 | 3.4% |
| Others | 1,796 | 6.1% |
Important Cyber Security Vulnerabilities Statistics 2025
In the 2024 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR), vulnerability exploitation was identified as the initial point of entry in 14% of all breaches, marking a significant increase from previous years.
Application breaches, often involving stolen credentials and vulnerabilities, accounted for 25% of all breaches in 2024, based on multiple sources.
Here is an overview based on available data.
- As of 31st May 2024, approximately 6% of all published CVEs had been exploited in the wild.
- The average CVSS score for CISA KEV (Known Exploited Vulnerabilities) listed vulnerabilities, was 8.4.
- 53% of scored CVEs discovered in 2024 were of High and Critical Severity.
The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) and the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVE) system have documented over 176,000 vulnerabilities to date—ranging from high-profile threats like CVE-2017-0144, a critical Windows SMB flaw, to widespread attacks such as the Mirai botnet, which exploited insecure IoT devices.
From January to mid-July, the number of reported CVEs rose by approximately 30%, increasing from 17,114 in 2023 to 22,254 in 2024.
So far in 2024, 0.91% of all reported vulnerabilities (around 204 CVEs) have been confirmed as weaponized. This means they are actively exploitable in the wild.
Primary Exploitation Vectors:
The most common attack methods for weaponized CVEs include:
- Exploiting public-facing applications for initial access
- Leveraging remote services for lateral movement across networks
Revival of Older Threats:
- Research shows a 10% increase in the weaponization of older CVEs (discovered before 2024).
Vulnerability Remediation & Notable CVE Highlights
Mean Time to Remediation (MTTR) Trends
- According to Edgescan, the average time to remediate internet-facing vulnerabilities is approximately 57.5 days, a slight improvement from the previous year’s 60.3 days.
- The MTTR varies significantly by industry:
- Public sector organizations: 92 days
- Healthcare sector: 44 days
- Notably, smaller organizations tend to resolve vulnerabilities faster than larger ones, likely due to fewer systems and leaner infrastructures.
Most Severe Vulnerability of 2021: CVE-2021-44228 (Log4Shell)
- Log4Shell impacted the Log4j logging library—widely used in Java-based applications and platforms.
- This critical vulnerability allowed attackers to execute arbitrary code on affected systems remotely.
- Despite prompt patching efforts, it’s believed that many unpatched instances still exist, making it a persistent threat across industries.
Oldest Vulnerability Still Discovered: CVE-1999-0517
- Originally identified in 1999, this vulnerability affects SNMPv2 (Simple Network Management Protocol v2).
- It allows unauthorized access via a guessed community string.
- With a CVSS score of 7.5, it’s categorized as a high-severity vulnerability and demonstrates how long-standing flaws can linger in legacy systems.
First Critical Cloud Vulnerabilities: January 2020
- In early 2020, Check Point researchers uncovered critical vulnerabilities in Microsoft Azure’s cloud infrastructure.
- These flaws received a perfect CVSS score of 10.0, qualifying them as “critical”.
- They showed that even hyperscale cloud environments aren’t immune, as the vulnerabilities could allow attackers to compromise the apps and data of other users sharing the same hardware.
Citrix Vulnerability Attacks Surged by 2,066% in 2020
According to Check Point, attacks targeting remote access solutions skyrocketed in 2020:
- Citrix vulnerabilities saw a 2,066% increase, a more than 20-fold rise.
- Attacks on Cisco products rose by 41%.
- VPN exploitation attempts jumped by 610%, and RDP by 85%.
Insight: The pandemic-driven shift to remote work drastically expanded attack surfaces.
31% of Companies Detected Exploitation Attempts in 2020
A Positive Technologies report found that nearly one-third of organizations identified attempts to exploit known software vulnerabilities.
- Over 50% of these attempts targeted CVE-2017-0144 (SMBv1)—the flaw exploited by WannaCry ransomware.
Despite a patch released in 2017, unpatched systems continued to be prime targets even 3.5 years later.
84% of Companies Expose High-Risk Vulnerabilities on External Networks
Another Positive Technologies study revealed that 84% of organizations had high-risk vulnerabilities on their network perimeters.
- Shockingly, over half of these vulnerabilities could be resolved simply by applying available security updates.
This highlights a widespread lack of basic patch management, especially in internet-facing assets.
26% of Companies Still Vulnerable to WannaCry
According to Positive Technologies, over one in four organizations (26%) have yet to patch the vulnerability exploited by the WannaCry ransomware—even years after its peak.
Notably, WannaCry attacks spiked again in Q1 2021, underscoring how legacy threats remain a major security concern.
Never Let Hackers Win the Game with Early Detection and Prevention of Potential Cyber Threats with ZeroThreat Contact Us to Start
XSS Continues to Dominate Vulnerability Reports
Research from HackerOne revealed that Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) was the most commonly reported vulnerability in 2020, accounting for 23% of all submissions.
- Other leading weaknesses included:
- Information Disclosure – 18%
- Improper Access Control – 10%
XSS persists as a top vector for injection attacks, particularly in web and SaaS environments.
Computer Software Tops Bug Bounty Earnings
When it comes to bug bounty payouts, the computer software industry offers the highest rewards for ethical hackers.
- Average payout for critical vulnerabilities:
- Computer Software: $5,754
- Electronics & Semiconductors: $4,633
- Cryptocurrency & Blockchain: $4,481
These figures highlight where researchers focus their efforts—and where organizations should prioritize defenses.
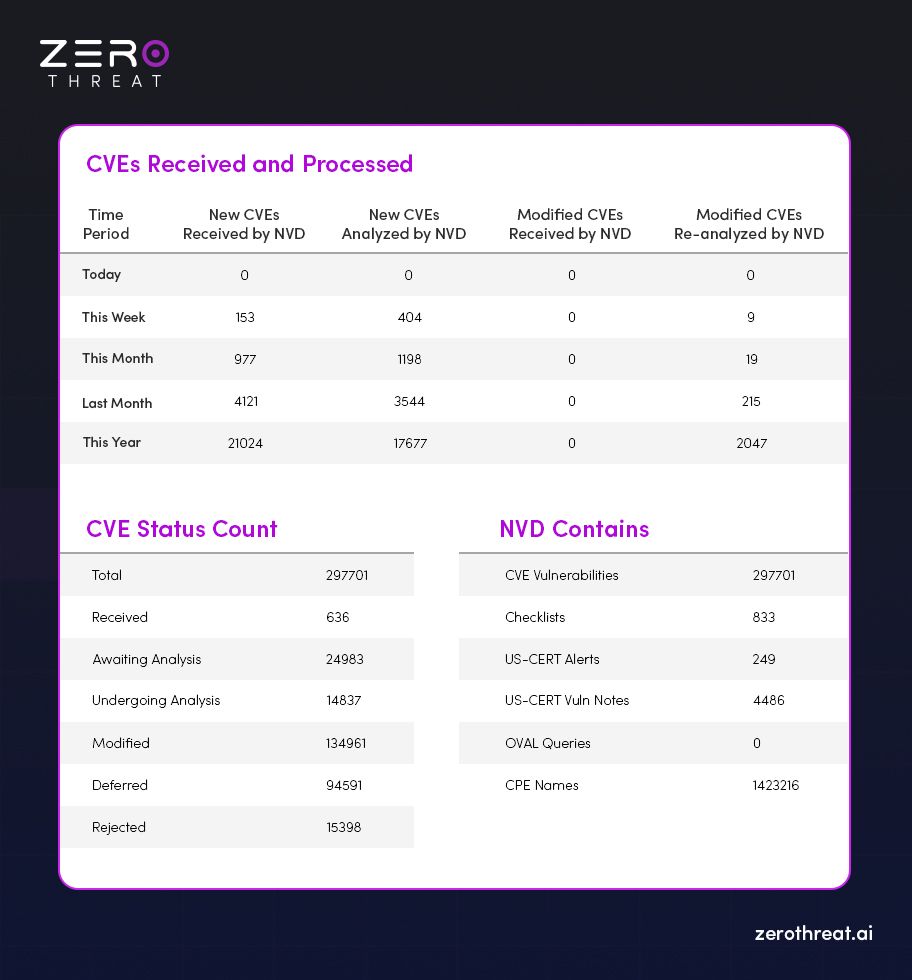
Vulnerability Volume in 2025
- The National Vulnerability Database (NVD) recorded 297,701 total entries in 2025.
- In just Q1 2025, 17,677 new vulnerabilities were listed—indicating the rapid pace of threat discovery.
Exploit-to-CVE Lag is a Major Concern
- Alarmingly, 80% of exploits are published before their associated CVEs are officially released.
- On average, there's a 23-day gap between exploit publication and CVE disclosure—leaving a critical window for attackers to act before defenders are alerted.
Legacy Vulnerabilities Still Being Exploited
- In 2021, 18% of attacks targeted vulnerabilities originally listed in 2013 or earlier.
- Even more concerning: 75% of attacks were carried out using vulnerabilities that had been exposed in or before 2017.
This emphasizes the urgent need for organizations to manage and remediate long-known issues—not just the latest threats.
Widespread Presence of High-Risk Vulnerabilities
- A study revealed that 84% of companies have high-risk vulnerabilities in their environments.
- Half of these could be mitigated simply by applying available software updates.
Unpatched Systems Lead to Breaches
- A staggering 60% of data breaches are caused by the failure to apply known patches—a preventable issue that remains one of cybersecurity’s biggest weaknesses.
Exponential Growth in Vulnerabilities
- 25,000 CVEs per year
According to University research, in June 2025, over 25,000 new Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs) are cataloged annually.
- Daily disclosure rate ~115 CVE/day
Mid‑2024 data show an average of 115 vulnerability disclosures per day—up ~30% from the previous year.
- 240,000+ vulnerabilities indexed
As of November 2024, the CVE database contained more than 240,000 entries.
Sectors, Platforms & Attack Vectors
- Microsoft Office—most exploited target
Between Nov 2021 and Oct 2023, >70% of cyberattacks targeted Microsoft Office; browsers (12%) and Android (6%) were also frequent targets.
- Web app vulnerabilities rampant
98% of web applications are vulnerable to some kind of attack.
- Unpatched vulnerabilities drive breaches
84% of companies harbor critical vulnerabilities, half of which could be mitigated with simple patches, and failure to apply patches causes ~60% of breaches.
Exploitation Velocity & Scale
- Fastest breakouts ever recorded (51 sec)
CrowdStrike reports a record-breaking ~51-second eCrime breakout time.
- AI-driven scanning: 36,000 scans/sec globally
Fortinet data reveals a 16.7% increase year-over-year in automated scans, now exceeding 36k per second.
- Malware-free threats rising
CrowdStrike logs show 79% of detections in 2024 were malware-free.
Economic Stakes
- Cybercrime cost → $10.5 trillion by 2025
Projected global cost of cybercrime reaches US$10.5 trillion in 2025, with a projected $23 trillion by 2027.
- Average data breach cost ~US$4.88 million
In 2024, the average cost per data breach hit US$4.88 million, marking a 10% YoY increase.
- Healthcare sector hit hardest
Ransomware grew by 264% over 5 years; average healthcare breach cost: US$10.1 million.
National & Regional Insights
- India: only 7% of organizations cyber-ready
Cisco's 2025 index shows just 7% of Indian orgs are equipped to handle modern (AI-augmented) cyber threats.
- EU launches own vulnerability database
After seeing some 40,000 annual CVE submissions to U.S. systems—with 100+ daily reports and 1 critical each day—the EU enacts its own database to reduce dependency.
Detection and Severity of Vulnerabilities
- A 2020 World Economic Forum report revealed a shockingly low vulnerability detection rate of just 0.05% in the U.S., signaling a significant gap in proactive threat identification.
- 43% of cyberattacks target small businesses, yet only 14% are adequately prepared to defend against them, exposing a serious readiness gap in the SME sector.
- Organizations with fewer than 100 employees tend to have the lowest number of critical or high-severity vulnerabilities, likely due to smaller and simpler IT environments.
- In contrast, enterprises with over 10,000 employees face the highest volume of critical vulnerabilities, reflecting the complexity and scale of their infrastructure.
- On average, 4.6% of vulnerabilities in web applications are classified as critical, while 4.4% are high severity—indicating a consistent, measurable risk in web-facing systems.
- For applications that process payment card data, the share of critical vulnerabilities rises to 8%, highlighting the heightened risk in financial transaction environments.
- Over 33% of discovered vulnerabilities across the full technology stack were categorized as critical or high severity, underlining persistent risks from top to bottom—application to infrastructure.
- SQL Injection (CWE-89) continues to be the most prevalent critical web application vulnerability, maintaining its top position since 2022.
- Application/API: high/critical severity: average MTTR 74.3 days.
- Device/network vulnerabilities: high/critical severity: average MTTR 54.8 days.
- A total of 40,009 CVEs were published in 2024—a record high and a reflection of the growing complexity in software and hardware ecosystems.
- The CISA Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog contained 1,238 vulnerabilities by the end of 2024, with 185 added during the year
- 768 CVEs were publicly reported as exploited for the first time in the wild in 2024, representing 2% of all discovered vulnerabilities and a 20% increase from 2023.
- A Veracode study found that 80% of organizations fail to address newly discovered flaws within the first 18 months after an initial scan.
- Over time, vulnerabilities become more persistent—especially in older software, where fixes are applied less frequently, and maintenance often declines.
- Around 70% of applications still contain at least one known vulnerability even after five years in production.
- In 2022, 19% of all scanned software was found to have high or critical severity vulnerabilities, representing a major concern for organizations with aging codebases and insufficient patch management.
Critical Application Security and Threat Exposure Stats
- 76% of all applications have at least one known vulnerability, highlighting the widespread gaps in secure software development practices.
- 1 in 5 organizations still do not test their software for security flaws, leaving systems highly exposed to preventable threats.
- 80% of public exploits are made available before the corresponding CVEs are officially released, giving attackers a dangerous head start.
- 80% of cyberattacks continue to exploit vulnerabilities that are three years old or more, showing that old flaws remain highly relevant.
- A staggering 84% of companies have high-risk vulnerabilities on their network perimeter, which could be easily leveraged for initial access.
- 69% of modern malware now targets zero-day vulnerabilities, underlining how rapidly evolving threats are outpacing traditional defense measures.
Leverage AI-powered AppSec to Discover Critical Vulnerabilities and Safeguard Your Applications Test Your App Now
Final Thoughts: From Awareness to Action
It’s right to say that in 2025, cybersecurity is no longer about whether you’ll face a vulnerability, but how fast you can detect, assess, and respond.
In a year where 25,000 new vulnerabilities emerge and attacks scale in seconds, the only way to stay safe is to stay ahead with automation, intelligence, and speed.
ZeroThreat was built for this reality.
By leveraging dual AI engines and fully autonomous AppSec capabilities, ZeroThreat identifies vulnerabilities faster than ever before—10x quicker with over 98.9% accuracy—and dramatically reduces false positives. Our platform continuously scans even complex, authenticated environments, integrates directly into CI/CD pipelines, and provides actionable AI-generated remediation insights.
Instead of drowning in CVEs and chasing patch cycles, ZeroThreat empowers your team to focus only on what matters—critical, real threats that put your data and users at risk.
In a year where threat velocity defines survivability, ZeroThreat doesn’t just help you keep up—it keeps you ahead.
Ready to see where you stand?
- Run a Free Vulnerability Scan: https://app.zerothreat.ai/
- View Pricing: https://zerothreat.ai/pricing
- Contact Our Security Experts: https://zerothreat.ai/contact-us
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


