All Blogs
Deepfakes & AI Phishing in 2025: Alarming Stats You Can’t Ignore

Quick Summary: Explore how deepfake scams and AI-generated phishing are redefining cyber threats in 2025. Backed by the latest statistics, this blog reveals alarming trends, financial impacts, and how advanced platforms like ZeroThreat can defend against next-gen attacks.
Cyberattacks have entered an alarming new phase, where the lines between reality and manipulation blur with frightening ease. Well, it’s all because of advancements in Gen AI. Threat actors are now deploying ultra-realistic deepfake videos and hyper-personalized phishing emails at unprecedented scale and sophistication. These are not just clever tricks but powerful tools capable of breaching multi-billion-dollar enterprises, deceiving financial institutions, and impersonating voices with chilling accuracy.
From AI-generated voice scams that mimic CEOs to phishing emails crafted by LLMs that outsmart spam filters and fool trained professionals, the threat landscape is evolving faster than most organizations can keep up.
This blog uncovers the most critical phishing attack statistics from 2025, shedding light on how deepfake and AI-powered phishing are reshaping cybersecurity. And what we must do to prepare.
Automated AI-powered Vulnerability Scanning – Test Smarter, Not Harder with ZeroThreat! Check the Pricing List
On This Page
- Deepfake Statistics
- Deepfake Fraud Statistics
- Deepfake Scams Statistics
- Deepfake Crime Statistics
- Impact of Deepfake
- Deepfake Types
- Deepfake Purpose & Intent
- Key Phishing Statistics in 2025
- Top Phishing Attacks Statistics
- Phishing Trends
- AI-Generated Phishing Statistics
- Vishing & Smishing
- Cybersecurity & Phishing Threat Statistics 2025
- AI Voice Cloning Statistics
- Industries Most Impacted by Deepfake Attacks and Phishing
- Geographical Distribution of Attacks
- Technological Tools Used by Attackers
- Defensive Measures and Counter-strategies
- Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead?
- Final Thoughts
Deepfake Statistics in 2025
Cybercriminals are increasingly taking advantage of our instinct to trust and help others, using deepfaked (cloned) voices to deceive individuals and steal thousands of dollars. But it didn’t end there. Deepfake fraud is rapidly escalating, targeting both individuals and businesses on a global scale.
Let’s go through deepfake scams and deepfake statistics.
- 63% of cybersecurity leaders express concern about AI being used to generate deepfakes, citing it as a rising threat to digital trust.
- Only 71% of people globally are aware of what deepfakes are, and just 0.1% can reliably detect them, indicating a major gap in public awareness.
- 98% of all deepfake videos found online are pornographic, highlighting how the technology is being overwhelmingly misused.
- The financial sector remains a prime target, with 53% of financial professionals reporting deepfake scam attempts as of 2024.
- In Q1 of 2025 alone, there was a 19% increase in deepfake incidents compared to the total for all of 2024.
- Leading up to the 2024 U.S. elections, 77% of voters encountered deepfake content involving political candidates.
- 72% of enterprises are concerned about deepfake risks in the future—up from 48% today.
- 43% of enterprises say investing in deepfake protection will be a top priority in the next 12-18 months.
- Despite ongoing initiatives, 60% of organizations don’t feel prepared to combat deepfake threats.
- Deepfakes now account for 6.5% of all fraud attacks, marking a staggering 2,137% increase since 2022, and emphasizing the need for robust risk mitigation.
- YouTube is the most common platform for encountering deepfakes, with 49% of users reporting exposure to deepfake content.
- In Hong Kong, a finance firm was scammed out of $25 million after AI technology deepfaked the voice and appearance of the company’s CFO during a video call.
- Deepfake spear phishing attacks have surged over 1,000% in the past decade, expanding their reach and targeting a broader range of victims across sectors.
- In 2024, approximately 60% of individuals reported encountering at least one deepfake video online.
- 1 in 10 companies admitted they had been directly targeted by deepfake-enabled phishing or impersonation attacks.
- 71% of people worldwide surveyed by iProov admitted they do not know what deepfakes are, revealing a major gap in global awareness of this technology. Among those aware, there is a wide variance in confidence levels when it comes to identifying deepfakes accurately, highlighting the need for better education and training.
- According to a survey by Sapio Research, 46% of organizations view generative AI as a cybersecurity threat, stating that it has increased their exposure to deepfake phishing attacks and other AI-enabled risks.
- 60% of consumers reported encountering a deepfake video within the last year, signaling widespread exposure to manipulated content. Only 15% of respondents claimed they have never come across a deepfake, indicating that such content has become nearly unavoidable.
- Human accuracy in detecting deepfake images averages just 62%, underscoring the limitations of visual analysis. When it comes to high-quality deepfake videos, humans correctly identified them only 24.5% of the time, showing how realistic and deceptive these videos have become.
- Deepfake fraud attempts surged by 3,000% in 2023, fueled by the growing accessibility of generative AI tools that enable scammers to easily create convincing fake content. On average, deepfake-related fraud costs businesses nearly $500,000, with some large enterprises facing losses as high as $680,000 in 2024.
- DeepFaceLab, an open-source tool on GitHub, is responsible for over 95% of all deepfake videos created globally. It uses artificial neural networks to mimic the visual and auditory characteristics of original content.
- DeepFaceLab powers over 95% of deepfake videos globally through its open-source platform.
- According to McAfee, 70% of people aren’t confident they can distinguish between a real and AI-cloned voice. Yet, 40% say they would respond to a voicemail from a loved one asking for help—a vulnerability criminals exploit.
- Just a small voice sample is enough for scammers to trick victims’ families, and 1 in 10 people have received such cloned messages. Of those, 77% lost money.
- With 53% of people sharing their voice online weekly—via YouTube, social media, or podcasts—cybercriminals have no shortage of audio to exploit.
- Just 3 seconds of audio can generate an 85% accurate voice clone, making voice-based scams alarmingly easy to execute.
- False or misleading content spreads faster than factual news, with the top 1% of Twitter (now X) rumors reaching up to 100,000 people, while truthful stories rarely exceed 1,000.
- Deepfake video creation costs range from $300 to $20,000 per minute, depending on complexity and the prominence of the person being faked.
- According to Sumsub, deepfake fraud rose 10x from 2022 to 2023, with 88% of cases occurring in the crypto sector and 8% in fintech.
- North America saw a 1,740% increase in deepfake fraud in 2022, while the Asia-Pacific region rose by 1,530%, reflecting regional surges in sophisticated digital impersonation.
- CEO fraud now targets at least 400 companies daily, posing a serious threat to businesses unprepared for advanced deepfake-enabled scams.
- As per business.com, over 10% of companies have experienced attempted or successful deepfake fraud, with some suffering damages equal to 10% of their annual profits.
- 1 in 4 company leaders have little to no understanding of deepfake technology, which may explain why 31% of executives believe deepfakes pose no added fraud risk.
- 80% of companies lack any formal protocols to respond to deepfake attacks, leaving them highly vulnerable.
- More than half of business leaders admit their teams aren’t trained to recognize or respond to deepfake threats.
- Just 5% of company leaders say they have a comprehensive deepfake prevention strategy in place—covering staff awareness, communication safeguards, and operational procedures.
Deepfake Fraud Statistics
- 1 in 4 business leaders have little to no familiarity with deepfake technology, despite AI’s rising influence in cyber threats.
- 31% of executives underestimate the risk, believing deepfakes haven’t increased their company’s exposure to fraud.
- 32% of leaders lack confidence in their employees’ ability to detect or respond to deepfakes effectively.
- Over 50% of business leaders admit their teams have never received training on identifying or mitigating deepfake attacks.
- 1 in 10 executives say their company has already faced deepfake-based threats, with another 10% unsure if they’ve been targeted.
- In the past year, deepfake detection surged 10x across all industries, emphasizing the rapid advancement of AI-driven fraud.
- 88% of deepfake cases in 2023 were concentrated in the crypto sector, making it the most targeted industry.
- Fintech saw a 700% increase in deepfake incidents in 2023, highlighting growing exploitation of financial systems.
- North America experienced a staggering 1,740% rise in deepfake fraud in 2023, reflecting a sharp regional escalation.
- Fraud losses from generative AI technologies in the U.S. are projected to hit $40 billion by 2027, rising from $12.3 billion in 2023 at a compound annual growth rate of 32%.
Deepfake Scams Statistics
90% of mobile threats in Q1 2024 stemmed from scams, phishing, and malvertising, with attackers increasingly using AI-driven deception techniques.
According to Avast’s Q1 2024 Threat Report, cybercriminals are weaponizing deepfakes and AI-synced audio—especially on platforms like YouTube, where hijacked channels spread fraudulent content using fake visuals and voices.
In 2023, 60% of Americans ranked deepfakes as their top AI-related concern, above all other risks tied to artificial intelligence.
Synthetic media like deepfakes present a double-edged sword—while they enable innovation in entertainment and translation, they also erode trust in digital content due to their misuse in disinformation and fraud.
Current deepfake detection tools struggle, with only a 65% success rate against advanced platforms such as DeepFaceLab and Avatarify.
Cybersecurity analysts have noted a rise in dark web chatter about using tools like DeepFaceLab to bypass identity verification by manipulating selfies and videos.
65% of Americans are concerned about AI-driven privacy violations
A 2024 survey reveals that 65% of Americans are worried about how AI technologies could misuse personal data, reflecting increasing anxiety over digital privacy and surveillance risks.
Deepfake Crime Statistics
Deepfake face swap attacks on ID verification systems rose by 704% in 2023.
Cybercriminals are increasingly using face swap deepfakes and virtual cameras to bypass remote identity verification, highlighting a sharp rise in sophisticated attacks.
By 2026, 30% of enterprises will consider standalone identity verification tools unreliable.
According to Gartner, the surge in AI-generated deepfake trends is forcing companies to rethink their approach to face biometric authentication.
66% of cybersecurity professionals encountered deepfake-related security incidents in 2022, a 13% increase from 2021.
This rise reflects the growing impact of deepfakes on cybersecurity operations and incident response.
92% of executives expressed serious concerns about the risks of generative AI.
A 2023 cross-industry survey revealed that most business leaders are alarmed by the threats posed by generative AI technologies.
Over 80% of professionals viewed deepfakes as a business risk in 2021, yet only 29% of firms had protective measures in place, and 46% lacked any mitigation strategy.
This gap between awareness and action highlights a major vulnerability across industries.
More than 80% of insurance professionals are concerned about manipulated digital media, but only 20% have taken action against deepfake threats.
This 2022 finding reveals a stark discrepancy between perceived risk and preparedness in the insurance sector.
Hunt Every Vulnerability in Your Applications and APIs Before Hackers Hunt Them to Steal Your Data Start Scanning Now
Impact of Deepfake
| Category | Key Statistics |
|---|---|
| Monthly attacks | From 4–5 to hundreds |
| DIY costs | ~$5 and 10 min per scam |
| Crypto firm losses | $440k avg, 57% hit |
| Single-call heist | $25.6M (HK) |
| Australian impact | 20% target rate, $25M loss |
| Fintech large losses | 25% hit over $1M |
| Consumer exposure | 80% images, 64% videos, 48% audio |
| Reporting rate | 22% report exposure |
| Business detection confidence | 42% only somewhat confident |
| Demand for alerts | 62% want alerts |
| Detection improvement | +8% by pausing to verify |
Crypto firms hit hard: In 2024, 57% of crypto companies faced audio deepfake incidents, averaging $440,000 in losses.
Banking losses in Hong Kong: A single incident involving a deepfake video call led to a $25.6 million payout.
Australian businesses targeted daily: 20% of companies reported deepfake scams in the past year, with one case costing AU$37 million (~US $25M).
Fintech sees major hits: Nearly 25% of fintech firms reported over $1 million in deepfake fraud losses, double the global average of around $450,000–$603,000.
Human intuition still effective: In controlled tests, humans outperform AI detectors in identifying deepfakes.
General mistrust remains: Nearly half of businesses (42%) only feel somewhat confident in detecting deepfakes
Geo-specific risk awareness:
- Mexico: 83% worry about video deepfakes, 85% about audio
- Financial leaders: 66% see audio deepfakes as a moderate-to-high threat
Westfield High School, New Jersey (2023): Male students generated sexually explicit deepfake images of their female classmates, raising alarm about the ease of targeting minors with AI manipulation.
Pennsylvania Cheer Squad Scandal (2021): A mother used deepfake technology to fabricate images of her daughter’s cheerleading rivals appearing nude and intoxicated. The images were sent to a coach, resulting in the wrongful suspension of a student believed to be depicted using marijuana.
Pikesville High School, Maryland: In an attempt to discredit the principal, an athletic director created a fake audio recording portraying the school leader making racist remarks—highlighting how deepfakes can be weaponized in workplace vendettas.
Criminals increasingly use deepfakes to deceive high-value organizations. Two notable examples include:
- Arup Incident (2024): A deepfake impersonation of the British engineering firm Arup’s CFO resulted in a $25 million transfer to Hong Kong-based accounts. The scam included a video call featuring AI-generated visuals of the CFO and other fake employees.
- U.K. Energy Firm Case (2019): Cybercriminals used a deepfaked voice of the company’s CEO to trick an employee into transferring €220,000 to an external bank account.
Deepfake technology has also made its way into the political arena, with several high-profile incidents in the U.S.:
- New Hampshire Voter Suppression Attempt (2024): Thousands of voters received robocalls featuring a deepfaked voice resembling President Biden, urging them not to vote in the state’s primary. Shockingly, the audio cost just $1 and took under 20 minutes to produce.
- Nancy Pelosi Video Manipulation (2019): A low-quality deepfake video of House Speaker Nancy Pelosi appearing impaired went viral, amassing over 2.5 million views on Facebook. Despite its rudimentary production, the clip misled a large audience, underscoring the persuasive power of deepfakes in political misinformation.
Other significant deepfake incidents include:
- Bank Voice Authentication Breach (2023): A journalist successfully bypassed his bank’s security by using a deepfake of his own voice, exposing vulnerabilities in voice-based authentication.
- Fake Drake & The Weeknd Collaboration (2023): A deepfake track featuring AI-generated vocals of Drake and The Weeknd circulated widely on streaming platforms, despite neither artist being involved.
- Elon Musk Crypto Scam (2022): A deepfake video of Elon Musk falsely promised investors 30% daily returns for life, luring victims into a cryptocurrency scam.
- "Queen Elizabeth II" Holiday Message (2020): A fabricated video showed a digitally recreated Queen Elizabeth II delivering a surreal Christmas message, raising concerns about media trust.
- "President Nixon" Apollo 11 Disaster Speech: A deepfake project brought to life a contingency speech Nixon never delivered, imagining a tragic end to the moon landing mission.
- AI "Salvador Dalí" at Florida Museum: A lifelike deepfake of the late artist welcomed visitors, even pausing to take selfies—blurring the line between tech-powered art and digital resurrection.
Deepfake Types
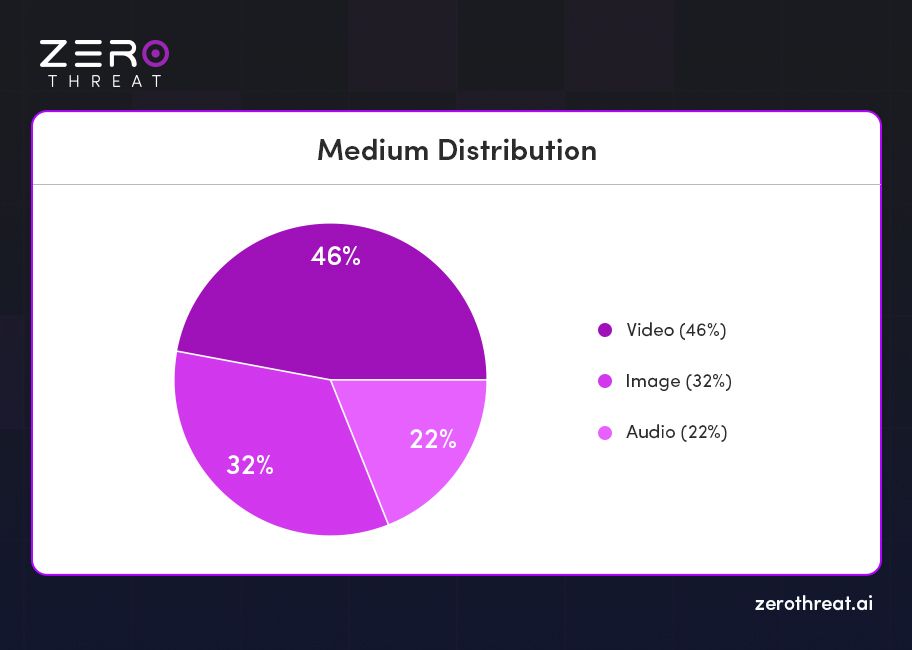
In 2025, deepfake technology has advanced to a highly sophisticated level, with video formats leading the way—accounting for 46% of all deepfake content. Their emotional impact and high potential for virality make them the most exploited format. This is followed by images at 32% and audio at 22%, highlighting a growing trend in the manipulation of multiple media types for deception and fraud.
Purpose and Intent
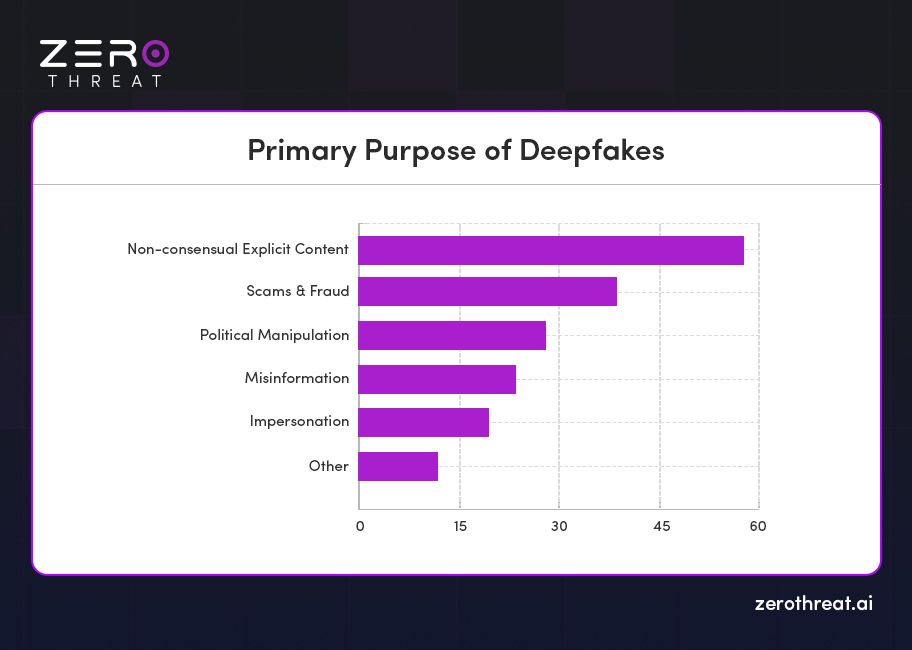
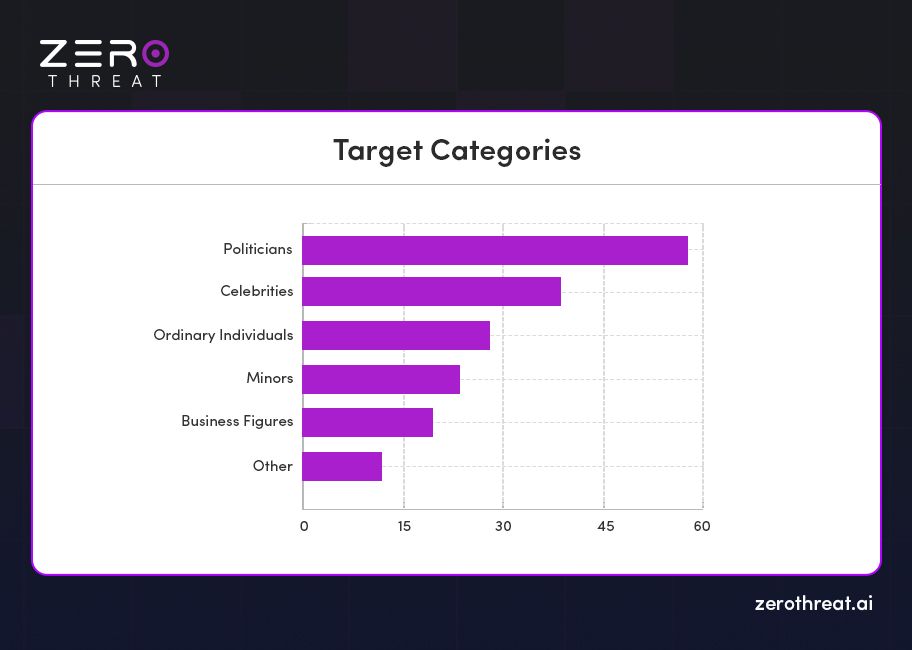
Analysis of our deepfake incident database reveals that synthetic media technologies are being leveraged across a wide range of malicious activities. However, a few key categories dominate the threat landscape, including fraud and financial scams, political misinformation, non-consensual explicit content, and identity spoofing. These uses not only highlight the growing accessibility of deepfake tools but also the urgent need for stronger detection systems and regulatory safeguards.
Every Minute of Delay is a Ticking Time Bomb for Security, Act Now to Test and Uncover Hidden Weaknesses and Prevent Costly Data Breaches! Contact Our Team for Help
Key Phishing Statistics in 2025
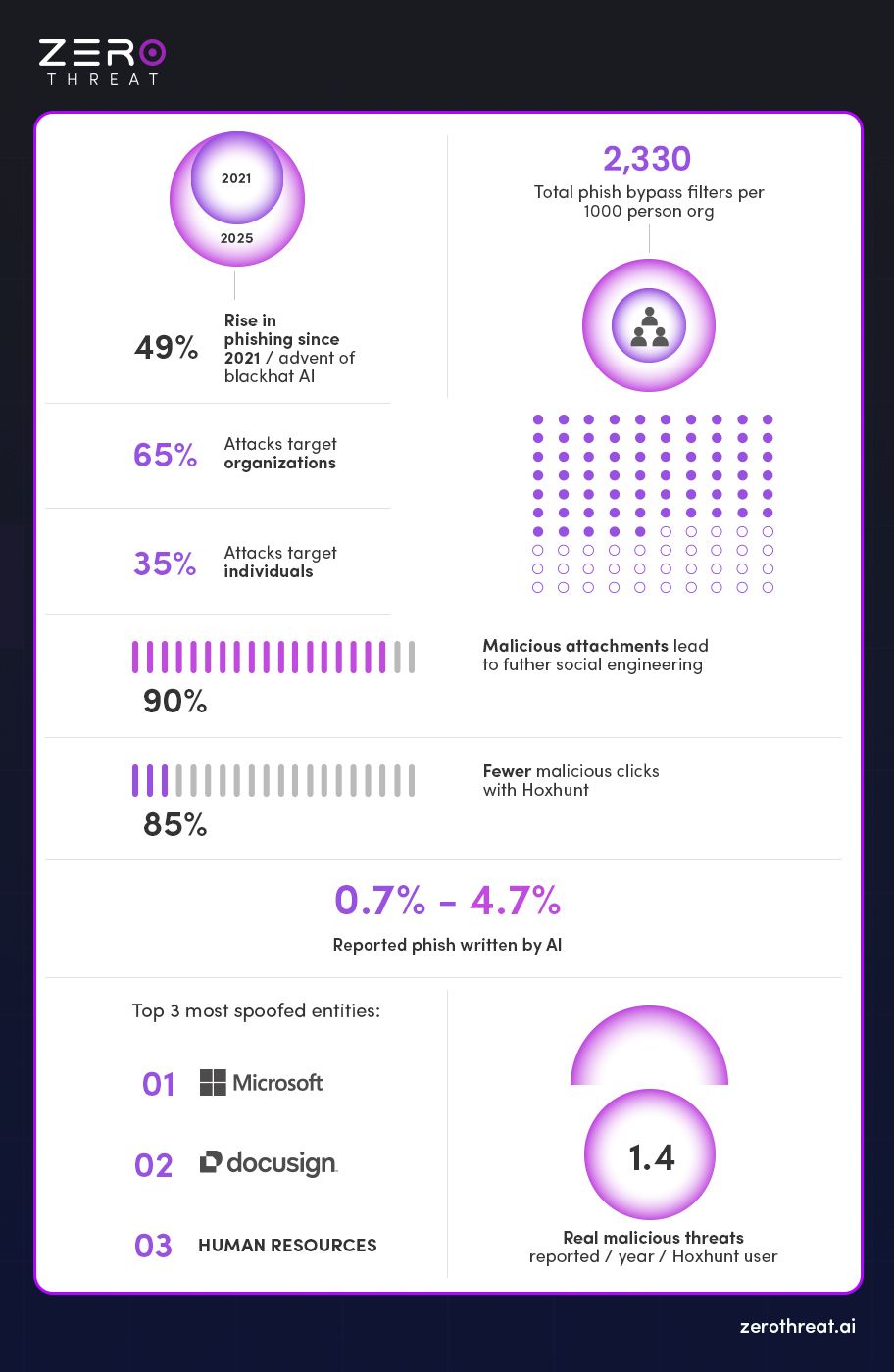
- According to the 2024 IBM / Ponemon Cost of a Data Breach study, the average annual cost of phishing rose by nearly 10% from 2024 to 2023, from $4.45m to $4.88m. That's the biggest jump since the pandemic.
- Phishing continues to be the leading vector for cyberattacks, with most breaches originating from deceptive emails.
- According to GreatHorn, 57% of organizations encounter phishing attempts on a weekly or daily basis. With 1.2% of all emails classified as malicious, this equates to an alarming 3.4 billion phishing emails sent every day.
- Human error remains a critical vulnerability—contributing to 60% of security breaches, as revealed by the Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) 2025.
- Supporting this, CSO Online reports that 80% of all security incidents are linked to phishing, with global losses reaching $17,700 every minute, underscoring the massive financial impact of this persistent threat.
- In 2022, phishing attacks in the U.S. alone resulted in the compromise of 300,497 accounts, causing losses of over $52 million.
- Phishing is responsible for 36% of all data breaches in the U.S., making it a leading cause of corporate compromise.
- An overwhelming 83% of organizations face at least one phishing attack every year.
- Between 2020 and 2021, there was a staggering 345% increase in the number of unique phishing websites.
- The average cost of a phishing attack for corporations has risen to $4.91 million, factoring in financial loss, downtime, and reputational damage.
A survey by Statista found that ransomware infections were caused by:
- 54% Phishing
- 27% Poor user practices / gullibility
- 26% Lack of cybersecurity training
- 14% Malicious websites
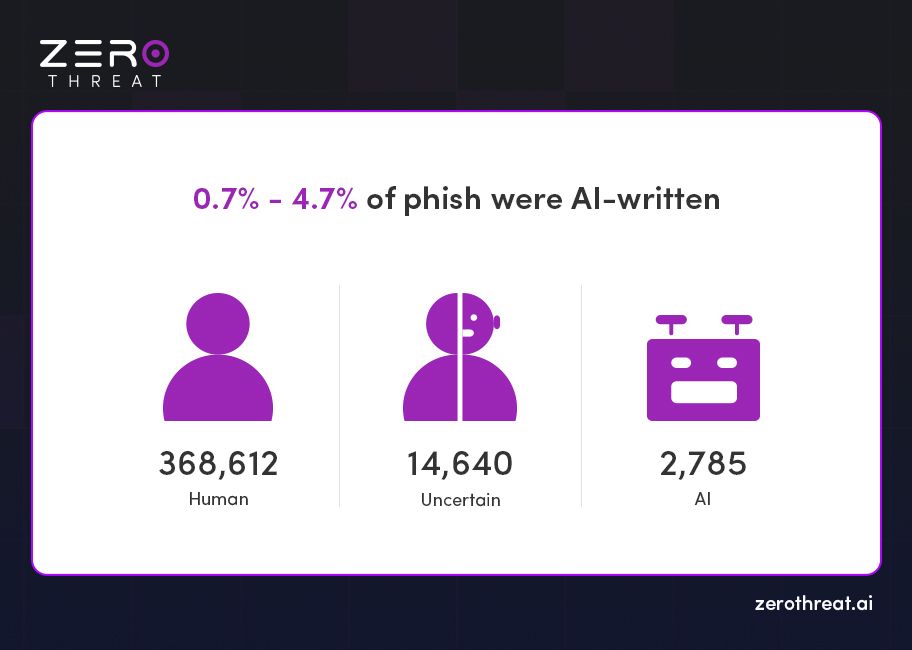
A 2024 analysis by Hoxhunt of 386,000 malicious phishing emails that reached employee inboxes revealed a surprising insight: only 0.7% to 4.7% of these phishing emails were identified—or suspected—to be written by AI. This suggests that, despite the rapid rise of generative AI, most phishing attacks still rely on traditional human-crafted tactics, although the role of AI phishing is expected to grow significantly in the near future.
Top Phishing Attacks Statistics
Staying informed about the latest phishing attack statistics is essential for navigating today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape. Awareness of these trends can help organizations better prepare, defend, and respond to emerging threats.
Here are some of the most eye-opening phishing attack statistics you should know in 2025:
- Phishing continues to be the #1 cyber threat, initiating the majority of security breaches across industries.
- 83% of organizations worldwide reported experiencing at least one phishing attack this year.
- 57% of companies face phishing scams on a weekly or daily basis.
- Over 3.4 billion phishing emails are sent every day, accounting for 1.2% of total global email traffic.
- The average cost of a phishing attack for corporations reached $4.91 million, factoring in data loss, recovery, and downtime.
- 36% of U.S. data breaches are directly caused by phishing attacks.
- Human error remains a weak link, contributing to 60% of all breaches, as per the Verizon DBIR 2025.
- 80% of security incidents are linked to phishing, causing global financial losses of $17,700 every minute.
- Phishing emails grew 202 % in H2 2024, while credential phishing surged 703 %—largely driven by AI-crafted campaigns
- AI‑generated phishing emails, compared to human-crafted ones, achieved 54 % click-through, versus just 12 % for manual attacks
- Spear‑phishing generated by LLMs (e.g., GPT‑4) gained 56 % click-through, matching skilled human attackers and outperforming generic emails by 350 %
- In 2022, the U.S. reported 300,497 compromised accounts and $52 million in losses from phishing alone.
- Between 2020 and 2021, there was a 345% surge in unique phishing websites.
- According to Hoxhunt’s 2024 analysis, only 0.7% to 4.7% of phishing emails were confirmed or suspected to be written by AI — showing that human-crafted scams still dominate.
- 44% of people believe an email is safe if it contains familiar branding — a vulnerability cybercriminals exploit. In 2022, over 30 million malicious emails used Microsoft branding alone.
- Telephone-oriented attack delivery (TOAD) attempts surged, with 300,000–400,000 calls daily in 2022, peaking at 600,000 per day in August.
- Direct financial losses from phishing increased by 76% in 2022, showing how much more damaging successful attacks have become.
- User reporting blocked 75 million threats, with roughly 1 in 10 threats intercepted due to vigilant individuals.
- According to F5 Labs, 55% of phishing websites use targeted brand names to deceive users and steal sensitive information more effectively.
- 84% of U.S. organizations report that regular security awareness training has reduced employee susceptibility to phishing attacks.
- In Australia, 92% of companies experienced a successful phishing breach — a 53% increase compared to 2021.
- The most impersonated brands in phishing attacks include Google and Amazon (13%), WhatsApp and Facebook (9%), and Apple and Netflix (2%).
- According to IBM’s 2022 Data Breach Report, phishing-related breaches took an average of 295 days to detect and contain — the third longest among all breach types.
- Phishing accounted for 16% of all breaches and had an average cost of $4.91 million, making it the second most common cause of data breaches.
Phishing Trends
Financial Institutions Under Fire
According to APWG, 23% of phishing attacks in Q2 2023 targeted financial institutions, followed closely by SaaS platforms and social media at 22.3% each.
Deceptive Links Reign Supreme
Cloudflare’s analysis of 13 billion emails shows that 36% of phishing threats involved deceptive URLs, making this the most common tactic.
Brand Impersonation Still Dominant
Phishers frequently mimic Microsoft, Google, and Amazon, with 51.7% of malicious emails disguised as coming from these trusted names (Cloudflare).
AI-Enhanced Phishing Surging
Zscaler ThreatLabs highlights a sharp rise in AI-generated phishing emails that mimic human tone and grammar, making detection increasingly difficult.
Ransomware's Favorite Delivery Method
Phishing remains the top vector for ransomware, initiating 35–45% of attacks. Email defenses are now critical for ransomware mitigation.
AI-Powered Email Scams
Cybercriminals use AI tools and chatbots to create flawless, typo-free emails that closely resemble legitimate business messages.
Exploitation of Cloudflare Services
Threat actors are abusing Cloudflare Workers and Pages to host phishing payloads, increasing email legitimacy and bypassing filters.
Smishing Goes Global
Organized cybercrime groups like the Smishing Triad are running large-scale SMS phishing operations, linked to over 200,000 fake domains.
Hyper-Personalized AI Attacks
AI phishing now leverages public personal data to create messages impersonating friends or family, making scams harder to spot—even for savvy users.
AI-Generated Phishing Statistics
- 57% of organizations face phishing attempts daily or weekly.
- New hires are 44% more vulnerable to phishing and social engineering within their first 90 days.
- 1.2% of all daily emails—around 3.4 billion messages—are malicious.
- 74% of breaches involve human error or social engineering tactics.
- Phishing is responsible for 80% of reported security incidents.
- Phishing losses total $17,700 per minute for businesses worldwide.
- 23% of phishing attacks target financial institutions, with 22.3% aimed at social media and SaaS platforms.
- Deceptive links remain the top phishing method, accounting for 36% of all threats.
- 51.7% of phishing emails impersonate trusted brands like Microsoft and Google, making them harder to detect.
- 35% of ransomware attacks now originate from phishing emails.
- AI-generated phishing emails are increasingly human-like and harder to detect.
- A new phishing site goes live every 20 seconds globally.
- 91% of security managers believe traditional training isn’t enough to stop phishing threats.
- 493.2 million phishing attacks occurred in Q3 2023 alone—a 173% surge from the previous quarter.
- Facebook topped the list of most impersonated brands in phishing URLs in 2023.
- 89% of phishing emails bypassed authentication protocols like SPF, DKIM, and DMARC.
- 35.6% of phishing attacks rely on users clicking malicious links, the most common delivery method.
- 50% of phishing emails now include attachments (e.g., PDFs, QR codes) to avoid detection.
Vishing & Smishing: The Rising Threat of Phone-Based Cybercrime in 2025
- As per Keepnet, 70% of organizations unknowingly disclosed sensitive information during vishing (Voice Phishing) simulations, underscoring major human-factor vulnerabilities.
- $14 million is the average annual cost of vishing attacks per organization—highlighting the financial impact of phone-based fraud.
- Customer support teams are the most frequently targeted, due to their frequent external communication and access to sensitive data.
- 6.5% of users fell for simulated vishing calls, pointing to a persistent gap in voice-based threat awareness.
- 40.3% of employees avoided answering vishing calls—either out of caution or inadvertently ignoring potential security alerts.
- Companies that deploy advanced vishing simulation platforms report the lowest compromise rates, proving the value of proactive training.
- Vishing attacks have risen 30% year-over-year, making voice-based social engineering a top priority for cyber defense.
- 76% of businesses faced smishing attacks (SMS phishing) in the last year, with incidents spiking by 328% and average losses of $800 per attack globally.
- $39.5 billion was lost to phone scams last year, placing vishing among the most damaging fraud tactics globally.
- Senior citizens saw a 40% rise in vishing attacks over two years, making them a prime target for scammers exploiting trust and digital inexperience.
Perform Automated Scans with 40,000+ TTPs to Identify Critical Security Risks and Safeguard Your Data Get Instant Access
Cybersecurity & Phishing Threat Statistics 2025
- 48% of phishing emails in January 2025 included malicious attachments, emphasizing the ongoing evolution of email-based threats.
- Ransomware tops the list of cyber threats, with 45% of cybersecurity leaders ranking it as their primary organizational risk.
- Phishing and BEC attacks are a close second, with 20% of leaders identifying cyber-enabled fraud as their top concern.
- Supply chain disruption remains a key vulnerability for 17% of security executives, revealing growing concerns over third-party exposures.
Cyber Risk Priorities for 2025
- 37% of leaders cite identity theft as their biggest concern.
- 24% are most worried about compromised personal data.
- 20% each flagged cyber extortion and loss of utilities as major threats.
AI, Deepfakes & Emerging Threats
- 47% of organizations now view AI-powered adversarial attacks as their primary GenAI risk.
- 42% experienced a phishing or social engineering attack in 2024, with expectations of growth as AI tools become more accessible to attackers.
- The dark web trade in deepfake tools surged 223% between Q1 2023 and Q1 2024, reflecting the growing commercialization of AI-powered deception.
- 55% of CISOs regard deepfakes as a moderate-to-severe threat to their organization’s security posture.
Scam Farms, BEC, and the Rise of Generative AI Usage
- Cybercriminal scam-farms have stolen more in the 12 months prior to mid-2024 than any previous year, according to Keepnet.
- Business Email Compromise (BEC) led to $6.3 billion in losses, with a median loss of $50,000 per incident.
- 15% of employees accessed generative AI tools, and 72% of those did so via personal email accounts, raising concerns around data governance.
Breach Vectors: What’s Fueling Incidents?
- Ransomware was involved in 44% of breaches, with a median payout of $115K. Notably, 64% of victims refused to pay.
- 30% of breaches stemmed from third-party compromises.
- 22% were linked to stolen credentials, while 20% exploited known vulnerabilities.
- Edge and VPN vulnerabilities surged 8x, with only 54% patched and a median remediation time of 32 days.
- Espionage-related breaches climbed 163%, now making up 17% of all incidents.
Human Factor & Infostealer Surge
- 60% of breaches involved human error, though user-reported threats quadrupled following security training.
- Infostealers targeted 30% of corporate devices and 46% of unmanaged devices holding stored credentials—making credential theft a widespread risk.
AI Voice Cloning Statistics
- Cybercriminals are increasingly turning to AI-powered voice cloning, which uses real voice recordings to generate convincing fake audio.
- This tech is now a key tool in phone phishing scams, making AI-driven fraud more deceptive and harder to detect.
- 1 in 10 adults worldwide has encountered an AI voice scam.
- 77% of those targeted reported financial losses from these scams.
- Over half (53%) of adults share voice data online at least once a week.
- Adults aged 60+ are 40% more likely to fall victim to voice cloning scams, especially those with access to sensitive data like login credentials or financial information.
- Studies show people can only detect AI-generated voices correctly 60% of the time.
- The global AI voice cloning market was valued at $2.1 billion in 2023 and is projected to hit $25.6 billion by 2033.
- In April 2024, a LastPass employee was targeted with a voice-cloned message impersonating CEO Karim Toubba—but fortunately, the scam failed.
Industries Most Impacted by Deepfake Attacks and Phishing
Certain industries have become prime targets for deepfake and AI-generated phishing attacks due to the sensitivity of data and potential financial gains.
Top 5 Targeted Sectors in 2025:
- Financial Services (28%)
- Deepfake voice calls impersonating executives.
- AI-generated invoices and BEC scams.
- Healthcare (19%)
- Fake patient portals and telehealth sessions.
- Credential harvesting via AI-tailored emails.
- Government & Public Sector (17%)
- Disinformation campaigns using deepfake videos.
- Phishing attacks against civil servants.
- Legal & Professional Services (15%)
- Law firms targeted for client data via AI spear-phishing.
- Deepfake impersonation in courtrooms or legal negotiations.
- Retail & E-commerce (12%)
- AI-generated fake product reviews and influencers.
- Phishing through personalized shopping offers.
Geographical Distribution of Attacks
While cybercrime knows no borders, certain regions have seen disproportionate levels of deepfake and AI-generated phishing activity.
| Region | % of Global Incidents |
|---|---|
| North America (39%) | Highest per capita losses; major focus on BEC and executive impersonation. |
| Europe (26%) | Europe (26%) Rising deepfake disinformation campaigns during elections. |
| Asia-Pacific (21%) | High use of AI phishing in banking and e-commerce sectors. |
| Latin America (9%) | Increasing ransomware-as-a-service with AI components. |
| Middle East & Africa (5%) | State-sponsored deepfake campaigns and political manipulation. |
Technological Tools Used by Attackers
Cybercriminals in 2025 are leveraging both open-source and commercial AI tools to execute their attacks.
Commonly Used Technologies:
- Stable Diffusion v6, Runway ML, and Synthesia – For creating deepfake videos.
- ElevenLabs, iSpeech, and Resemble AI – For generating synthetic voice clones.
- ChatGPT-5, Claude 3, and LlamaGuard – For crafting persuasive phishing emails.
- DarkBERT – An underground version of BERT trained on dark web data for phishing lures.
- DeepFaceLab, FaceSwap, and First Order Motion Model – For video deepfakes.
Additionally, attackers are using zero-day exploits and AI evasion techniques to bypass traditional detection systems.
Defensive Measures and Counter-strategies
Organizations and governments are responding with advanced countermeasures, though many still lag behind the pace of innovation.
Emerging Defense Mechanisms:
- Digital Watermarking: Embedding invisible identifiers in AI-generated content (e.g., Meta's “AI watermark” initiative).
- Behavioral Biometrics: Analyzing speech patterns, typing rhythms, and facial micro-expressions to detect fakes.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Especially critical in mitigating deepfake voice fraud.
- AI-Powered Email Filters: Solutions like Darktrace Antigena and Microsoft Defender for Office 365 now integrate AI threat detection.
- Employee Training Programs: Simulated phishing and deepfake recognition drills.
- Legislative Frameworks: Laws such as the EU’s AI Act, U.S. DEEPFAKES Accountability Act, and China’s Generative AI Regulation aim to regulate misuse.
- Collaborative Threat Intelligence Platforms: Sharing indicators of compromise (IOCs) across industries.
Despite these efforts, adoption remains uneven. Only 31% of SMEs have implemented AI-specific cybersecurity measures, according to a 2025 OECD report.
Future Outlook: What Lies Ahead?
Looking ahead, experts predict several trends:
- Deepfake-as-a-Service (DaaS) will expand, lowering the technical barrier for entry-level attackers.
- AI vs AI: We’ll see a rise in adversarial AI systems where attackers and defenders deploy competing AI models.
- Regulatory Pressure: Governments may mandate labeling of all AI-generated content, similar to GDPR-style regulations.
- Decentralized Identity Systems: Blockchain-based digital IDs may help authenticate real identities in real time.
- Quantum Machine Learning: Could offer new ways to detect anomalies in AI-generated content.
By 2026–2027, the cost of AI-fueled cybercrime could reach $12 trillion annually, up from $8 trillion in 2022, according to Cybersecurity Ventures. The stakes have never been higher.
Don’t Wait for a Breach, Test Your App and Protect It Against Potential Cyberattacks Now Ready to Scan
Final Thoughts
The 2025 cyber landscape makes one thing clear: traditional defenses are no match for AI-generated deception. Only proactive, adaptive, and intelligence-driven security strategies can keep pace with this new era of cyber threats.
By strengthening application security through advanced penetration testing and continuous risk assessment, ZeroThreat helps organizations close critical gaps before attackers exploit them.
Powered by advanced AI models like GPT-4 Turbo and Gemini Ultra, ZeroThreat delivers automated, continuous application security testing. With features like advanced vulnerability detection, near-zero false positives, live AI-powered remediation reports, and support for MFA and complex environments, ZeroThreat helps organizations stay several steps ahead of evolving threats.
When AI is used to attack, it takes smarter AI to defend. With ZeroThreat, you don’t just detect risks—you outthink them.
Ready to fight deepfakes with facts and phishing with foresight?
Get a free vulnerability scan plan or Contact Us to see how ZeroThreat makes your app security future-ready.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is deepfake phishing?
Deepfake phishing uses AI-generated audio, video, or images to impersonate trusted individuals. These realistic fabrications deceive victims into revealing sensitive information, transferring money, or clicking malicious links, making it a dangerous evolution of traditional phishing attacks.
Are deepfakes used in phishing attacks?
How dangerous are AI phishing attacks?
How to identify a deepfake phishing attempt?
How much has deepfake phishing increased?
What are examples of deepfake phishing attacks?
Can AI be used to prevent phishing?
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


