All Blogs

Blog Synopsis: DoS and DDoS attacks are two very well-known attacks. But there is constant confusion about what they both are capable of doing and what makes them different from each other. In this blog, we have created differences that will help you understand the difference between DoS and DDoS more precisely and prevention practices to mitigate them. Let’s read this blog.
If you are running a large-scale business, then experiencing operational downtime can possibly be your biggest threat, as it acutely affects the business in multiple ways. But have you wondered what the root cause of dysfunctionality could be? Surprisingly, it's the attacker's job at times to cause website's server downtime. But how?
With the help of DoS and DDoS attacks, the attackers' job is done.
Attackers use Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks on a website's server, which leads to downtime. According to ITPro's research, in the first quarter of the previous year, there were 1.7 million HTTP DDoS attacks, 1.5 million DNS DDoS attacks, and 1.3 million L3/4 DDoS attacks. Isn't it alarming?
However, what puzzles the organization is understanding the differences between DoS and DDoS attacks. Knowing the difference can help you create a solid defense strategy. Moreover, protecting against both these attacks requires a proactive security approach that include vulnerability assessment besides traditional security measures like firewall, VPN, and stringent security control.
We have created this blog that covers all these aspects along with a full-fledged comparison of DoS and DDoS attacks. Get useful information to prevent such attacks and protect your business from potential downtime.
Are You Tired of Searching for Foolproof Security Solutions for Your Apps? We've Got You Covered Sign Up to Operate for Free
Table of Contents
- What is DoS Attack in Cybersecurity?
- How does Denial of Service (DoS) Attack Work?
- Main Types of DoS Attacks in Cybersecurity
- What is a DDoS Attack in Cybersecurity?
- How Does a Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attack Work?
- Main Types of DDoS Attacks
- Key Differences Between DoS and DDoS Attacks
- DoS and DDoS Attacks: 5 Powerful Prevention Tips
- The Bottom Line
What is DoS Attack in Cybersecurity?
A denial of service (DoS) attack occurs when a nasty entity tries to deliberately overload a computer system, website, or network with innumerable traffic or harmful requests, which causes the system to load slowly. The severity of the attack sometimes leads the system to become unresponsive or completely unavailable to users.
How does DoS Attack Work?
A Denial of Service attack does its job by overwhelming a system with too many malicious requests that consume its resources and cause dysfunctionality or server downtime. The attacker might flood the system with huge amounts of data to exhaust its bandwidth, misuse vulnerabilities in network protocols to crash services or overload certain applications with complex requests.
Main Types of DoS Attacks in Cybersecurity
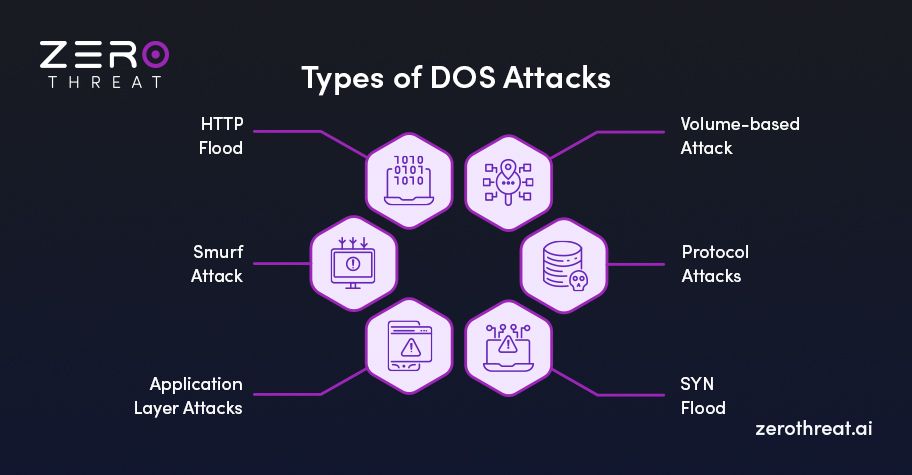
Let's get a better understanding of the types of DoS attacks examples to generate high-powered security for robust security.
1. Volume-based Attack
This type of attack overwhelms a website or a network with a huge amount of traffic, like processing an excessive number of data packets and causing exhaustion of systems bandwidth or a complete crash of a system.
2. Protocol Attacks
Protocol attacks aim to exploit vulnerabilities in network protocols or infrastructure. This type of attack includes sending malformed packets or exploiting protocol vulnerabilities to consume server resources or make a mess of network traffic.
3. SYN Flood
This type of attack misuses the TCP handshake process by sending too many SYN requests to a server without completing the handshake. This attack lavishly consumes server resources and disables them to process further authenticated requests.
4. Application Layer Attacks
This type of DoS attack targets particular applications or services, such as sending countless to a website's login page or API for it to be overloaded and crashed. This attack is often performed by exploiting vulnerabilities in the application itself.
5. Smurf Attack
This type of attack is performed by sending a great number of ICMP (ping) requests to a network's broadcast address, with the response directed at the victim by overwhelming it with the traffic.
6. HTTP Flood
This kind of attack is done by simulating legitimate excessive HTTP requests and ends up overwhelming the server, which results in slower server loading time or a complete crash.
What is a DDoS Attack in Cybersecurity?
A Distributed Denial of Service attack is done by misusing a network of compromised computers known as botnets. A DDoS attack is also performed to flood a target with overwhelming traffic. Unlike standard DoS attacks, which typically originate from a single source, a DDoS attack targets different compromised devices that are often parts of a botnet and work together to create an incredibly high amount of traffic on the website. This collective assault exhausts the targeted system's resources by exploiting its bandwidth, server capacity, or processing capacity. This auscultation disables the system to manage authenticated requests, which results in severe outages and service disruptions.
How Does DDoS Attack Work?
A Distributed Denial of Service attack is performed using a network of compromised computers, which is known as a botnet, to exhaust the targeted system with excessive traffic. These exploited devices, often infected with malware, are controlled by the attacker to send larger volumes of data or requests simultaneously. This collective flood of traffic overwhelms the target's servers, network infrastructure, or applications, and it consumes its resources and bandwidth. This results in excessively longer loading time, unresponsiveness, inaccessibility to registered users, and operational disruption.
Main Types of DDoS Attacks in Cybersecurity
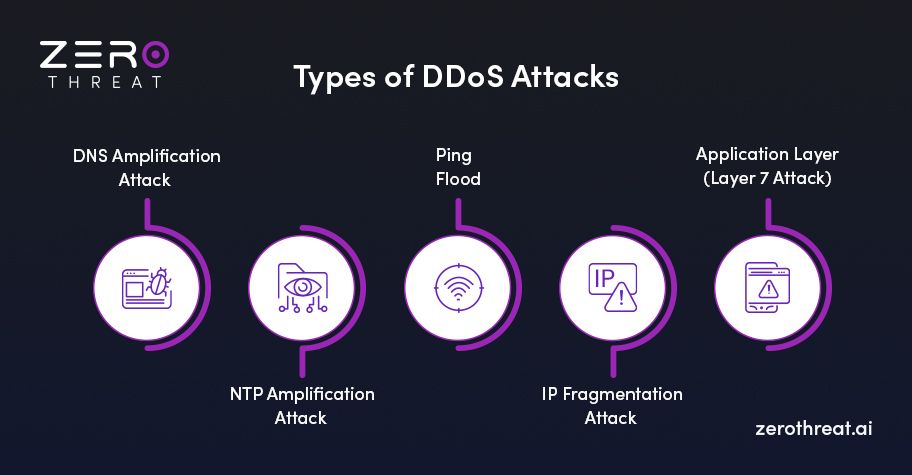
Let's dive deeper into the concept of Distributed Denial of Service attacks to craft equally robust solutions for their mitigation. Let's take a look.
1. DNS Amplification Attack
DNS attack aims to misuse the domain name system (DNS) to augment the volume of traffic sent to the target. The attacker sends DNS queries with a spoofed IP address to a DNS server. Because the response is much larger than the request, the DNS server sends a large response to the target by overwhelming it with traffic.
2. NTP Amplification Attack
This attack is similar to a DNS amplification attack; in this type of DDoS attack, Network Time Protocol (NTP) servers. Attackers send an NTP request with a spoofed source of IP address. The NTP server responds with a much larger response than the original request by amplifying the traffic sent to the target.
3. Ping Flood
The attack sends a huge number of ICMP echo requests (pings) to the targeted device or system. Their aim is to exhaust the network's bandwidth or the targeted system's capacity to manage incoming packets, which leads to Denial of Service or network congestion.
4. IP Fragmentation Attack
Using this attack, attackers send fragmented IP packets to the targeted system that are intentionally created in an improper way. The target system necessarily needs to compile them before processing them. This process consumes excessive time and resources and potentially crashes the system if it is unable to handle the large volume of fragmented traffic.
5. Application Layer (Layer 7 Attack)
These attacks target specific applications or services at the application layer (Layer 7 of the OSI model). They can send malformed requests or exploit application-specific vulnerabilities to crash or degrade the performance of web applications or services.
Security Threats are Evolving at a Great Speed. Let ZeroThreat Help You with Its High-level Assessment Use Automated Vulnerability Assessment
Key Differences Between DoS and DDoS Attacks
Let’s check out the key points of differences between Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks to learn how both attacks can cause damage to system’s performance and security. Let’s check out the table of differences.
| Points of Difference | DoS (Denial of Service) | DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | An attack that aims to make a service or network resource unavailable to its legitimate users by overwhelming it with a flood of illegitimate requests from a single source. | An attack where different systems (often part of a botnet) collectively flood a targeted system with traffic by overwhelming it to cause service unavailability. |
| Source | Single Source or IP Address | Various sources or IP addresses, typically from a network of compromised devices (botnet). |
| Scale | DoS attacks are generally small in scale; limited by the capacity of the single attacking source. | DDoS attacks are comparatively larger in scale. They merge the bandwidth and processing power of multiple compromised systems. |
| Complexity | They are generally less complex; often rely on uncomplicated methods like flooding or resource exhaustion from a single point. | They are more complex as they include coordinated attacks from different sources and high-level attacking techniques to escape detection. |
| Impact | They are limited to the capabilities of the single attacker; it may be easier to fix by blocking the attacking IP. | They are severe and tougher to fix due to the diversity of sources and the higher volume of traffic. |
| Detection | DoS are easier to identify and examine because of the single source of traffic. | DDoS are challenging to detect and fix because the attack traffic comes from numerous, often disparate, sources. |
| Attack Origin | DoS originates from a single machine or a small number of machines within the same network. | DDoS originates from a huge number of machines spread across multiple locations, often controlled by a botnet. |
DoS and DDoS Attacks: 5 Powerful Prevention Tips
Now that we have learned all the important insights about DoS and DDoS attacks, it's time to learn how to prevent them from disrupting the system's performance and services. Let's check out these proven tips.
1. Perform Traffic Filtering
Use firewalls to monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on pre-decided security protocols. Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS) can examine traffic for suspicious patterns and automatically block them.
2. Rate Limiting
Set thresholds on how many requests a single IP can make within a specific period of time. This can significantly help businesses alleviate the risk of automated attacks. Also, implement API rate limiting; if you provide APIs, ensure they are protected with rate limits to avoid abuse from automated scripts and ensure robust API security.
3. Load Balancing
Use load balancers to evenly allocate incoming requests across different servers. This prevents any single server from being overwhelmed. Deploy global load balancing to route users to the nearest data center and decrease latency and potential overload on specific servers.
4. Redundancy and Failover
Host services across different data centers in different geographic locations. If one goes down due to an attack, the others can begin with their job of maintaining service availability.
Also, implement automatic failover to backup systems when an attack is identified by ensuring minimal downtime.
5. Use DDoS Protection Services
Services like Cloudflare, Akamai, and AWS Shield specialize in DDoS protection. They can absorb great volumes of traffic and filter out harmful requests before they reach your servers.
DDoS mitigation services can scrub incoming traffic in real time by eliminating malicious data while alleviating traffic flow.
Let Attackers Give Up Trying to Do Your System's Exploitation Give Shot to our DAST Tool
The Bottom Line
Now that you have understood the difference between DoS and DDoS, the types of DDoS attacks, and their prevention practices, you are just a step away from defending against such critical attacks by implementing robust practices. All you need to do is to meticulously implement the steadfast security practices.
The good news is that you can alleviate the complexity of cybersecurity practices with the help of an automated AI tool, ZeroThreat that scans for vulnerabilities in your web applications in minutes. This tool helps you achieve robust web app security and prevents potential attacks like DoS and DDoS.
ZeroThreat is an advanced DAST tool that runs a comprehensive assessment of vulnerabilities to help your system stay away from potential security threats.
This blazing-fast tool speeds up vulnerability detection in CI/CD pipelines by 10x using AI-driven web apps and API security testing. Basically, it's a bouncer of your web apps and APIs that guards them from nasty attacks without charging a penny! Sign Up to validate yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which attack is more serious, DoS or DDoS?
DDoS (Distributed Denial of Service) attacks are more serious than DoS (Denial of Service) attacks because they leverage multiple compromised systems to overwhelm a target, making them harder to mitigate and significantly more damaging.
Which types of tools should be used to mitigate DoS and DDoS attacks?
What is an RDoS – Ransom Denial of Service?
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


