All Blogs
CI/CD Security Testing for SaaS Team: Risks, Tools, and Best Practices

Quick Summary: CI/CD security testing helps SaaS teams ship faster without sacrificing security. This blog breaks down the top risks in modern pipelines, explores effective security testing tools, and best practices to protect code, secrets, and deployments. Whether you're scaling a startup or securing SaaS workflows, this guide will help you build safer, more resilient CI/CD pipelines from day one.
SaaS teams could deploy new features every week, sometimes every day. That rapid pace is great for business, but it also means your CI/CD pipeline becomes one of the most attractive targets for attackers. Recent research shows that around 40% of organizations now view CI/CD toolchain exposure as a significant risk.
So, what does that mean in real terms? It means a bug in your code, a misconfigured build script, or a leaked token can turn out to be a potential threat before your team notices it. The good part is that there are defined ways to secure your CI/CD pipeline without slowing down new deployments of your SaaS app.
In this blog, we’ll cover CI/CD security testing for SaaS applications, helping you understand the risks and how to secure your SaaS app. We’ll explore the tools you can use to detect vulnerabilities in CI/CD pipelines, along with learning the best practices to keep them secure and efficient.
Don’t wait for a breach. Sign up now and automate your CI/CD security testing. Start Now
On This Page
- What is CI/CD Security Testing in SaaS?
- Types of CI/CD Pipelines Used by SaaS Teams
- Top CI/CD Security Risks in SaaS Environments
- CI/CD Security Testing Tools for SaaS Applications
- How to Implement CI/CD Security Testing for SaaS Applications?
- CI/CD Pipeline Security Best Practices
- Wrapping Up
What is CI/CD Security Testing in SaaS?
CI/CD security testing in SaaS is the process of making sure your software delivery pipeline secure at every step. CI/CD (Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment) pipelines automate how code moves from a developer’s local server into production. But without proper security checks, that convenience becomes a potential threat.
In a SaaS environment, where deployments happen multiple times a day, you can't rely on manual reviews or occasional scans. That’s where CI/CD security testing keeps development, build, testing, and deployment stages secure with continuous automated checks. It ensures that each change in code, API, and workflow is tested for vulnerabilities before it goes live.
SaaS teams always prioritize CI/CD security testing because it allows them to:
- Catch SaaS security issues early (before the project is deployed to production).
- Scan vulnerabilities such as leaked secrets, insecure configs, and unvalidated code.
- Build a secure CI/CD pipeline without slowing down releases.
To put it simply, CI/CD security testing is one of the best ways to implement a shift-left security for your SaaS project.
Types of CI/CD Pipelines Used by SaaS Teams
In a SaaS environment, the type of pipeline you use can impact how quickly and safely you handle deployment risks. Here's a breakdown of the most common CI/CD pipeline types used by SaaS teams:
SaaS-Hosted CI/CD Pipelines
These are fully managed pipelines offered by platforms like GitLab CI/CD, CircleCI, and Bitbucket Pipelines. You don’t need to manage servers or build agents. Everything happens in the cloud. This is ideal for SaaS teams who want scalability, low maintenance, and built-in integrations.
Self-Hosted CI/CD Pipelines
Tools like Jenkins, TeamCity, or Bamboo run on your own infrastructure. You get more control over configurations, plugins, and security policies. But you’re also responsible for securing the entire setup, including servers, networks, credentials, and pipeline runners. It’s powerful but requires expertise in DevOps and security automation.
Container-Based CI/CD Pipelines
They are designed for apps shipped as containers (like Docker), often built and deployed using tools like Kubernetes, Argo CD, or Tekton. Each pipeline stage happens inside isolated containers, making it easier to control dependencies and avoid “works on my machine” issues. This type is popular for microservices-based SaaS platforms.
GitOps Pipelines
The GitOps pipeline is triggered based on Git operations. Each branch may have its own CI/CD workflow. GitOps tools like Flux or Argo CD sync code to environments automatically via Git commits. It’s a clean model for version control, but it needs strong RBAC (Role-Based Access Control) and commits signing to prevent unauthorized changes.
Microservices CI/CD Pipelines
Instead of a single pipeline for the whole app, each microservice has its own pipeline. This enables faster deployments and rollbacks for individual components. But it also introduces new security challenges, such as managing secrets and permissions across many moving parts.
Secure your SaaS app with our pentesting tool, detecting vulnerabilities 10× faster. Run a Quick Test
Top CI/CD Security Risks in SaaS Environments
Your CI/CD pipeline pushes every update, patch, and feature to production as they are updated. But the same that helps you ship fast can also push critical vulnerabilities into customer environments. Here are the most common CI/CD security risks that SaaS teams need to stay ahead of:
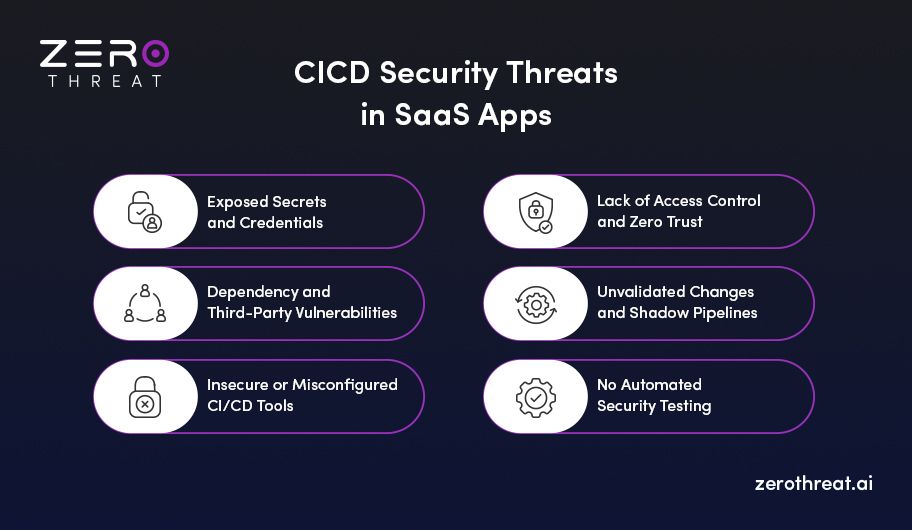
Exposed Secrets and Credentials
API keys, tokens, and database passwords often get stored in code repos, logs, or environment files without encryption. Once leaked, attackers can impersonate services, steal data, or pivot into your cloud infrastructure. You may use secret scanning and vault-based storage to secure your CI/CD pipeline against this attack.
Dependency and Third-Party Vulnerabilities
Modern SaaS apps rely heavily on open-source libraries and third-party services. If your pipeline isn’t continuously checking for vulnerable dependencies, you’re shipping risk with every deployment. Tools like SCA (Software Composition Analysis) help flag common CVEs, but they only work if integrated early in your CI/CD pipeline testing.
Insecure or Misconfigured CI/CD Tools
Many teams use hosted CI/CD services like GitHub Actions or GitLab CI without tightening access controls. Default permissions, overlooked configuration settings, and unpatched runners expose your build systems to attackers. Once they compromise the CI/CD tool, they can modify code, inject malware, or deploy backdoors into production.
Lack of Access Control and Zero Trust
If everyone from developers to interns has access to the production pipeline, you're opening the door to insider threats and accidental errors. CI/CD pipelines should use the principle of least privilege or say Zero Trust architecture. So that every tool, user, and script has the minimum access needed to perform its task and nothing more.
Unvalidated Changes and Shadow Pipelines
Sometimes, deployment scripts or workflows get added by teams without proper review. These “shadow pipelines” bypass normal security checks, creating blind spots where untested or vulnerable code can slip into production. Security testing in SaaS for CI/CD pipelines should validate every change from pull request to release.
No Automated Security Testing
If security tests only run after code merges in production, you’re already too late. Manual checks can’t cope with the continuous deployments a SaaS app requires. Pentesting tools can help you spot SQL injections, insecure APIs, or broken authentication before they cause damage.
CI/CD Security Testing Tools for SaaS Applications
Not all security tools are built for SaaS or CI/CD pipelines. To help you pick the right ones, here are the top tools that test your SaaS apps and pipelines without slowing down your releases.
ZeroThreat: Automated Penetration Testing for SaaS
ZeroThreat continuously runs automated pentests directly in your CI/CD pipeline, validating real exploitability across web apps and APIs. By integrating with platforms like GitHub Actions, Azure Pipelines, GitLab, and AWS, ZeroThreat allows SaaS companies to continuously monitor their applications for vulnerabilities. It helps SaaS teams uncover business logic flaws, broken access controls, and other risks that scanners often miss.
OWASP ZAP: Open-Source DAST for CI/CD
ZAP is a dynamic security testing tool that simulates real-world attacks by scanning your running app or staging environment. It integrates with CI/CD tools like Jenkins and GitHub Actions to automate DAST scans. It can be used at scale, but it requires some tuning for enterprise-scale apps.
GitLab Ultimate: Built-In Pipeline Security
GitLab’s Ultimate tier includes SAST, DAST, dependency scanning, secret detection, and container scanning built into the pipeline. It lets developers see and fix issues from a single dashboard, without leaving GitLab. Ideal for SaaS teams already using GitLab for version control and deployment.
Burp Suite: Scalable DAST for CI/CD
Burp Suite Enterprise Edition supports automated web app security testing with CI/CD triggers and recurring tests. It detects vulnerabilities like XSS, SQL injection, and session flaws, and feeds results into JIRA or GitHub Issues. Enterprise teams value its depth, but it needs tuning for custom apps.
Orca Security: Cloud Security for SaaS
Orca provides agentless cloud security that scans your entire cloud environment, including CI/CD workloads, for misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, and identity risks. It connects to AWS, Azure, and GCP in minutes, without deploying agents or scripts. Ideal for SaaS companies needing full cloud visibility and compliance without slowing down deployments.
Integrate security into your favorite tools without slowing down your workflow. View Integrations
How to Implement CI/CD Security Testing for SaaS Applications?
CI/CD security for SaaS applications needs a different mindset because the stakes are higher. With rapid release cycles and multi-tenant architectures, every code push and pipeline step becomes a potential attack surface. This makes CI/CD security one of the priority needs for SaaS apps.
Here are the steps to integrate CI/CD security testing in your SaaS development workflow:
1. Map Your Pipeline and Identify Attack Surfaces
The first step in securing any CI/CD pipeline is to know what you're working with. In SaaS apps, pipelines are often built over time, using different tools and services. If you haven’t mapped how everything flows, there’s a good chance you’re missing hidden vulnerabilities that attackers can exploit.
Here’s how to approach it:
- Start by listing every stage of the pipeline, from code commit to deployment and post-release monitoring. This gives you visibility across the entire workflow.
- Document every tool and service involved, like GitHub, Jenkins, Docker, or AWS. Each integration can introduce security risks if not properly managed.
- Track how secrets, tokens, and environment variables move across stages, so you know where reused and exposed sensitive data is stored.
- Map out data flows and access permissions, ensuring only trusted roles or systems can trigger builds or deployments.
2. Approach with Shift-Left Security Testing
Shift-left security means testing early and often, instead of waiting until the code hits staging or production. By moving tests closer to the development phase, you avoid vulnerabilities that slow down releases or put customer data at risk.
Here’s how to implement it:
- Run security tests directly in the development phase, such as SAST (static code analysis) and dependency scanning, so issues are caught before code is committed or merged.
- Add pre-commit checks or pre-merge hooks in your version control system to block insecure code from entering the pipeline.
- Use developer-friendly security tools that provide real-time feedback in IDEs or pull requests, making it easy to fix issues.
- Adopt security-focused coding standards and train dev teams to recognize high-risk patterns early in the process.
- Treat security bugs like any other code defects, prioritizing them in sprints instead of letting them pile up until the end.
3. Integrate Automated Security Scans into Your Pipeline
Automation is what makes CI/CD work, and security should be no different. By integrating an automated vulnerability scanning tool directly into your CI/CD workflow, you reduce the chances of deploying vulnerable code. It also ensures that every code change is tested with the same consistency.
Here’s how to make it work:
- Use tools that run automatically during build or deploy stages, like SAST, DAST, or SCA (software composition analysis).
- Trigger scans on every pull request or commit, so no code moves forward without being checked for injection flaws, secrets, misconfigurations, or unsafe dependencies.
- Incorporate container and infrastructure scans, especially if you’re deploying to Kubernetes or using IaC like Terraform.
- Reflect scan results into dashboards or alerts, so both developers and security teams can see what code or issues need fixing.
4. Test Both Code and Runtime Environments
In SaaS environments, threats can surface not just in the source code, but in how the app behaves after it’s deployed. Testing both the code and the live environment helps you catch vulnerabilities such as broken access controls or business logic flaws.
Here’s how to do it right:
- Run static tests (SAST, SCA) on your codebase to detect insecure coding patterns, outdated libraries, or known vulnerabilities.
- Add dynamic application security testing (DAST) in staging or pre-prod, so you can simulate real-world attacks against running apps and APIs.
- Use runtime security tools like RASP or agent-based monitors to detect unauthorized behavior or exploit attempts in production.
- Test environments with real configurations, including secrets, third-party integrations, or microservices, to find issues that don't show up in local dev.
- Validate business logic and permission flows, especially in multi-tenant SaaS apps where one user’s mistake shouldn't impact another.
5. Protect Secrets and Access in CI/CD
CI/CD pipelines are loaded with sensitive assets such as API keys, cloud credentials, SSH keys, database passwords. If even one of these leaks occurs, attackers can bypass your app security entirely and go straight for your infrastructure or data.
Here’s how to secure them:
- Use a secrets management tool like AWS Secrets Manager or GitHub Actions Secrets to store and inject sensitive values securely.
- Never hardcode credentials in code, configs, or environment variables, even in test or staging branches.
- Apply least-privilege access controls, so CI/CD tools only have permission to do what they need and nothing more.
- Rotate secrets and access tokens regularly, and automate the process where possible.
- Scan repos and pipelines for leaked credentials, using tools that detect exposed secrets before they hit prod.
6. Implement Continuous Monitoring and Alerting
Even the best CI/CD security testing can’t catch everything before deployment. That’s why real-time monitoring is a crucial part of securing SaaS apps. You need visibility into how your application behaves after each release so that you can spot abnormal activity or suspicious access.
Here’s how to stay ahead:
- Set up monitoring for both application and pipeline activity, including build failures, unauthorized code pushes, or unexpected config changes.
- Use security platforms that support real-time alerts, so your team knows immediately when something looks off.
- Add audit logs across tools like GitHub, Jenkins, and Kubernetes, to track who deployed what, and when.
- Use behavior-based alerts, not just static rules, so you can flag irregular patterns like sudden privilege escalation or unusual API calls.
- Integrate logs and alerts with your SIEM or Slack/Teams, ensuring alerts don’t get lost in the noise.
7. Run Security Tests on Every Environment, Not Just Prod
Security issues can start in development, staging, or even during a security fix. If you only test vulnerabilities in production, you're already too late. For SaaS enterprises that release frequently, running security tests across all environments ensures that threats are detected before they are exploited.
Here’s how to do it right:
- Run security scans during every stage, from development and QA to staging and pre-prod, not just before you go-live.
- Apply the same checks across environments, so vulnerabilities aren’t missed due to inconsistent security policies.
- Use isolated staging environments, built to mimic production as closely as possible, including real configs, permissions, and integrations.
- Incorporate automated regression testing, so the new code doesn’t break existing security controls.
- Monitor non-prod environments, since attackers often target dev or staging systems where controls are weaker.
CI/CD Pipeline Security Best Practices
Even with automation and testing in place, if your CI/CD pipeline isn’t built on strong security practices, your application can remain vulnerable. Here are the CI/CD security best practices you can follow to keep your application safe:
- Use version control for everything, including pipeline configs and infrastructure as code.
- Enforce least-privilege access across users, tools, and environment variables.
- Harden build agents and runners with patched OS images and restricted access.
- Automate scans for code, containers, and dependencies before each deployment.
- Require multi-factor authentication (MFA) for all CI/CD and source control systems.
- Log and audit every build and deploy action to spot misuse or anomalies in code.
- Isolate dev, test, and prod environments to reduce the attack surface in case of compromise.
- Continuously monitor your pipeline and test it for security misconfigurations or weak spots.
Need help with securing your SaaS application? Let’s get in touch. Connect With Us
Wrapping Up
CI/CD security testing is the backbone of reliable SaaS apps. As pipelines grow more complex and release cycles get tighter, every new feature shipped without proper testing becomes a potential exploit waiting to happen.
That’s why the smartest SaaS teams are prioritizing security in every stage of delivery instead of doing it at the end. From protecting secrets to validating changes in real time, secure CI/CD pipelines reduce the risk of breaches, downtime, and non-compliance.
So, start by securing one stage, one tool, and one workflow at a time. With the right approach, you can build a CI/CD process where speed and security move in sync, and your SaaS product stays both agile and secure.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can automation improve CI/CD security?
Automation helps detect vulnerabilities earlier by integrating security scans into every build or deployment. It reduces human error, speeds up feedback, and ensures consistent checks across all code and environments.
What is the difference between CI/CD pipeline testing and application security testing?
How often should SaaS teams run CI/CD security tests?
How do secrets get leaked in CI/CD pipelines, and how can this be prevented?
Explore ZeroThreat
Automate security testing, save time, and avoid the pitfalls of manual work with ZeroThreat.


